Suppression of Her2/neu expression through ILK inhibition is regulated by a pathway involving TWIST and YB-1
- PMID: 20838384
- PMCID: PMC3007675
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.366
Suppression of Her2/neu expression through ILK inhibition is regulated by a pathway involving TWIST and YB-1
Abstract
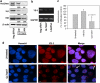
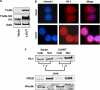
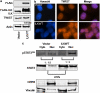
In a previous study it was found that the therapeutic effects of QLT0267, a small molecule inhibitor of integrin-linked kinase (ILK), were influenced by Her2/neu expression. To understand how inhibition or silencing of ILK influences Her2/neu expression, Her2/neu signaling was evaluated in six Her2/neu-positive breast cancer cell lines (LCC6(Her2), MCF7(Her2), SKBR3, BT474, JIMT-1 and KPL-4). Treatment with QLT0267 engendered suppression (32-87%) of total Her2/neu protein in these cells. Suppression of Her2/neu was also observed following small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of ILK expression. Time course studies suggest that ILK inhibition or silencing caused transient decreases in P-AKT(ser473), which were not temporally related to Her2/neu downregulation. Attenuation of ILK activity or expression was, however, associated with decreases in YB-1 (Y-box binding protein-1) protein and transcript levels. YB-1 is a known transcriptional regulator of Her2/neu expression, and in this study it is demonstrated that inhibition of ILK activity using QLT0267 decreased YB-1 promoter activity by 50.6%. ILK inhibition was associated with changes in YB-1 localization, as reflected by localization of cytoplasmic YB-1 into stress granules. ILK inhibition also suppressed TWIST (a regulator of YB-1 expression) protein expression. To confirm the role of ILK on YB-1 and TWIST, cells were engineered to overexpress ILK. This was associated with a fourfold increase in the level of YB-1 in the nucleus, and a 2- and 1.5-fold increase in TWIST and Her2/neu protein levels, respectively. Taken together, these data indicate that ILK regulates the expression of Her2/neu through TWIST and YB-1, lending support to the use of ILK inhibitors in the treatment of aggressive Her2/neu-positive tumors.
Figures


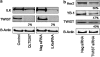
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A suppresses the expression of HER2 via a pathway involving TWIST and YB-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 1;6(1):207-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2702. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25402957 Free PMC article.
-
Using Pharmacokinetic Profiles and Digital Quantification of Stained Tissue Microarrays as a Medium-Throughput, Quantitative Method for Measuring the Kinetics of Early Signaling Changes Following Integrin-Linked Kinase Inhibition in an In Vivo Model of Cancer.J Histochem Cytochem. 2015 Sep;63(9):691-709. doi: 10.1369/0022155415587978. Epub 2015 May 4. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015. PMID: 25940338 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of IKKalpha/IKKbeta by integrin-linked kinase is required for HER2/neu-induced NF-kappaB antiapoptotic pathway.Oncogene. 2004 May 6;23(21):3883-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207485. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15021910
-
QLT0267, a small molecule inhibitor targeting integrin-linked kinase (ILK), and docetaxel can combine to produce synergistic interactions linked to enhanced cytotoxicity, reductions in P-AKT levels, altered F-actin architecture and improved treatment outcomes in an orthotopic breast cancer model.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(3):R25. doi: 10.1186/bcr2252. Epub 2009 May 1. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19409087 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): a "hot" therapeutic target.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1115-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00444-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007949 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel HIF-1α-integrin-linked kinase regulatory loop that facilitates hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 10;6(10):8271-85. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3186. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25821081 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Integrin-Linked Kinase in Modulating the Stemness of IL-6-Abundant Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating γ-Secretase-Mediated Notch1 Activation in Caveolae.Neoplasia. 2015 Jun;17(6):497-508. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.06.001. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26152358 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a novel integrin-linked kinase inhibitor.J Med Chem. 2011 Sep 22;54(18):6364-74. doi: 10.1021/jm2007744. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21823616 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A suppresses the expression of HER2 via a pathway involving TWIST and YB-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 1;6(1):207-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2702. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25402957 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNA-363 during tumor progression and invasion.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;80(3):481-499. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01022-1. Epub 2024 May 1. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38691273 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed N, Riley C, Oliva K, Stutt E, Rice GE, Quinn MA. Integrin-linked kinase expression increases with ovarian tumour grade and is sustained by peritoneal tumour fluid. J Pathol. 2003;201:229–237. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009a;10:430–436. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules. Curr Biol. 2009b;19:R397–R398. - PubMed
-
- Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP, Bouchet BP, Thomas C, et al. Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Bader AG, Vogt PK. Phosphorylation by Akt disables the anti-oncogenic activity of YB-1. Oncogene. 2008;27:1179–1182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

