5'-3'-UTR interactions regulate p53 mRNA translation and provide a target for modulating p53 induction after DNA damage
- PMID: 20837656
- PMCID: PMC2947767
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1968910
5'-3'-UTR interactions regulate p53 mRNA translation and provide a target for modulating p53 induction after DNA damage
Abstract
Optimal induction of p53 protein after DNA damage requires RPL26-mediated increases in p53 mRNA translation. We report here the existence of a dsRNA region containing complementary sequences of the 5'- and 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs) of human p53 mRNA that is critical for its translational regulation by RPL26. Mutating as few as 3 bases in either of the two complementary UTR sequences abrogates the ability of RPL26 to bind to p53 mRNA and stimulate p53 translation, while compensatory mutations restore this binding and regulation. Short, single-strand oligonucleotides that target this 5'-3'-UTR base-pairing region blunt the binding of RPL26 to p53 mRNA in cells and reduce p53 induction and p53-mediated cell death after several different types of DNA damage and cellular stress. The ability to reduce stress induction of p53 with oligonucleotides or other small molecules has numerous potential therapeutic uses.
Figures
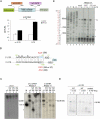
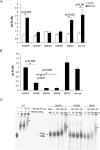
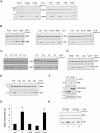
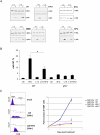
Comment in
-
Building p53.Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 15;24(20):2229-32. doi: 10.1101/gad.1988510. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20952532 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Interactions of nucleolin and ribosomal protein L26 (RPL26) in translational control of human p53 mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16467-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.349274. Epub 2012 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22433872 Free PMC article.
-
Building p53.Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 15;24(20):2229-32. doi: 10.1101/gad.1988510. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20952532 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin.Cell. 2005 Oct 7;123(1):49-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.034. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16213212
-
Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 at the RNA level.J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Jul;88(7):645-52. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0609-2. Epub 2010 Mar 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20306257 Review.
-
Translational Control in p53 Expression: The Role of 5'-Terminal Region of p53 mRNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 29;20(21):5382. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215382. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31671760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between 25S rRNA A loop and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B promotes subunit joining and ensures stringent AUG selection.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;33(18):3540-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00771-13. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23836883 Free PMC article.
-
Mdm2 and MdmX as Regulators of Gene Expression.Genes Cancer. 2012 Mar;3(3-4):264-73. doi: 10.1177/1947601912455331. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23150759 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Combinations of Untranslated-Region Sequences on Translation of mRNA.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 20;13(11):1677. doi: 10.3390/biom13111677. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002359 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring structural determinants and the role of nucleolin in formation of the long-range interactions between untranslated regions of p53 mRNA.RNA. 2023 May;29(5):630-643. doi: 10.1261/rna.079378.122. Epub 2023 Jan 18. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36653114 Free PMC article.
-
Translational control in cancer etiology.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a012336. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012336. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 22767671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashcroft M, Vousden KH 1999. Regulation of p53 stability. Oncogene 18: 7637–7643 - PubMed
-
- Franch T, Gultyaev AP, Gerdes K 1997. Programmed cell death by hok/sok of plasmid R1: Processing at the hok mRNA 3′-end triggers structural rearrangements that allow translation and antisense RNA binding. J Mol Biol 273: 38–51 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
