OpenMEEG: opensource software for quasistatic bioelectromagnetics
- PMID: 20819204
- PMCID: PMC2949879
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-9-45
OpenMEEG: opensource software for quasistatic bioelectromagnetics
Abstract
Background: Interpreting and controlling bioelectromagnetic phenomena require realistic physiological models and accurate numerical solvers. A semi-realistic model often used in practise is the piecewise constant conductivity model, for which only the interfaces have to be meshed. This simplified model makes it possible to use Boundary Element Methods. Unfortunately, most Boundary Element solutions are confronted with accuracy issues when the conductivity ratio between neighboring tissues is high, as for instance the scalp/skull conductivity ratio in electro-encephalography. To overcome this difficulty, we proposed a new method called the symmetric BEM, which is implemented in the OpenMEEG software. The aim of this paper is to present OpenMEEG, both from the theoretical and the practical point of view, and to compare its performances with other competing software packages.
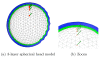
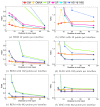
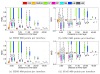
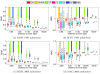
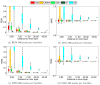
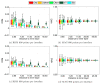
Methods: We have run a benchmark study in the field of electro- and magneto-encephalography, in order to compare the accuracy of OpenMEEG with other freely distributed forward solvers. We considered spherical models, for which analytical solutions exist, and we designed randomized meshes to assess the variability of the accuracy. Two measures were used to characterize the accuracy. the Relative Difference Measure and the Magnitude ratio. The comparisons were run, either with a constant number of mesh nodes, or a constant number of unknowns across methods. Computing times were also compared.
Results: We observed more pronounced differences in accuracy in electroencephalography than in magnetoencephalography. The methods could be classified in three categories: the linear collocation methods, that run very fast but with low accuracy, the linear collocation methods with isolated skull approach for which the accuracy is improved, and OpenMEEG that clearly outperforms the others. As far as speed is concerned, OpenMEEG is on par with the other methods for a constant number of unknowns, and is hence faster for a prescribed accuracy level.
Conclusions: This study clearly shows that OpenMEEG represents the state of the art for forward computations. Moreover, our software development strategies have made it handy to use and to integrate with other packages. The bioelectromagnetic research community should therefore be able to benefit from OpenMEEG with a limited development effort.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Forward field computation with OpenMEEG.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2011;2011:923703. doi: 10.1155/2011/923703. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21437231 Free PMC article.
-
Bioelectromagnetic forward problem: isolated source approach revis(it)ed.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Jun 7;57(11):3517-35. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/11/3517. Epub 2012 May 11. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22581305
-
Sensitivity of EEG and MEG measurements to tissue conductivity.Phys Med Biol. 2004 Mar 7;49(5):701-17. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/5/004. Phys Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 15070197
-
A survey on integral equations for bioelectric modeling.Phys Med Biol. 2024 Aug 28;69(17):10.1088/1361-6560/ad66a9. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad66a9. Phys Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39042098 Review.
-
Spatiotemporal EEG analysis and distributed source estimation in presurgical epilepsy evaluation.J Clin Neurophysiol. 1999 May;16(3):239-66. doi: 10.1097/00004691-199905000-00005. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1999. PMID: 10426407 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Source Imaging in Preclinical Rat Models of Focal Epilepsy using High-Resolution EEG Recordings.J Vis Exp. 2015 Jun 6;(100):e52700. doi: 10.3791/52700. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26131755 Free PMC article.
-
Altered correlation of concurrently recorded EEG-fMRI connectomes in temporal lobe epilepsy.Netw Neurosci. 2024 Jul 1;8(2):466-485. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00362. eCollection 2024. Netw Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38952816 Free PMC article.
-
Electroencephalography resting-state networks in people with Stroke.Brain Behav. 2021 May;11(5):e02097. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2097. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33759382 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial accuracy evaluation of magnetic source imaging methods on OPM-based MEG.iScience. 2022 Sep 22;25(10):105177. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105177. eCollection 2022 Oct 21. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36238897 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological investigation of the contribution of attention to altered pain inhibition processes in patients with irritable bowel syndrome.J Physiol Sci. 2020 Oct 6;70(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12576-020-00774-x. J Physiol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023474 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

