The beta/Gcd7 subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is crucial for binding eIF2 in vivo
- PMID: 20805354
- PMCID: PMC2953064
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00265-10
The beta/Gcd7 subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is crucial for binding eIF2 in vivo
Abstract
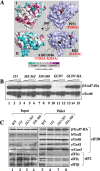
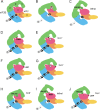
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B) is the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, which stimulates formation of the eIF2-GTP-Met-tRNA(i)(Met) ternary complex (TC) in a manner inhibited by phosphorylated eIF2 [eIF2(αP)]. While eIF2B contains five subunits, the ε/Gcd6 subunit is sufficient for GEF activity in vitro. The δ/Gcd2 and β/Gcd7 subunits function with α/Gcn3 in the eIF2B regulatory subcomplex that mediates tight, inhibitory binding of eIF2(αP)-GDP, but the essential functions of δ/Gcd2 and β/Gcd7 are not well understood. We show that the depletion of wild-type β/Gcd7, three lethal β/Gcd7 amino acid substitutions, and a synthetically lethal combination of substitutions in β/Gcd7 and eIF2α all impair eIF2 binding to eIF2B without reducing ε/Gcd6 abundance in the native eIF2B-eIF2 holocomplex. Additionally, β/Gcd7 mutations that impair eIF2B function display extensive allele-specific interactions with mutations in the S1 domain of eIF2α (harboring the phosphorylation site), which binds to eIF2B directly. Consistent with this, β/Gcd7 can overcome the toxicity of eIF2(αP) and rescue native eIF2B function when overexpressed with δ/Gcd2 or γ/Gcd1. In aggregate, these findings provide compelling evidence that β/Gcd7 is crucial for binding of substrate by eIF2B in vivo, beyond its dispensable regulatory role in the inhibition of eIF2B by eIF (αP).
Figures
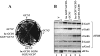

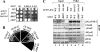
Similar articles
-
Identification of a regulatory subcomplex in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B that mediates inhibition by phosphorylated eIF2.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;16(11):6603-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.11.6603. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8887689 Free PMC article.
-
Tight binding of the phosphorylated alpha subunit of initiation factor 2 (eIF2alpha) to the regulatory subunits of guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B is required for inhibition of translation initiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):5018-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.5018-5030.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438658 Free PMC article.
-
eIF2 independently binds two distinct eIF2B subcomplexes that catalyze and regulate guanine-nucleotide exchange.Genes Dev. 1998 Feb 15;12(4):514-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.4.514. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9472020 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of eIF2B and insights into eIF2-eIF2B interactions.FEBS J. 2017 Mar;284(6):868-874. doi: 10.1111/febs.13896. Epub 2016 Sep 29. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27627185 Review.
-
Clues to the mechanism of action of eIF2B, the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor for translation initiation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Aug;36(Pt 4):658-64. doi: 10.1042/BST0360658. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18631136 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TAN1 (tRNA acetyltransferase) in eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B)-mediated translation control and stress response.3 Biotech. 2017 Jul;7(3):223. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-0857-8. Epub 2017 Jul 4. 3 Biotech. 2017. PMID: 28677085 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological dimerization and activation of the exchange factor eIF2B antagonizes the integrated stress response.Elife. 2015 Apr 15;4:e07314. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07314. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25875391 Free PMC article.
-
eIF2B Mechanisms of Action and Regulation: A Thermodynamic View.Biochemistry. 2018 Mar 6;57(9):1426-1435. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00957. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29425030 Free PMC article.
-
eIF2B is a decameric guanine nucleotide exchange factor with a γ2ε2 tetrameric core.Nat Commun. 2014 May 23;5:3902. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4902. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24852487 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the eIF2B regulatory subcomplex and its implications for the regulation of guanine nucleotide exchange on eIF2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Nov 16;43(20):9994-10014. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv930. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26384431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthony, T. G., J. R. Fabian, S. R. Kimball, and L. S. Jefferson. 2000. Identification of domains within the epsilon-subunit of the translation initiation factor eIF2B that are necessary for guanine nucleotide exchange activity and eIF2B holoprotein formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1492:56-62. - PubMed
-
- Boeke, J. D., J. Trueheart, G. Natsoulis, and G. R. Fink. 1987. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 154:164-175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
