Mechanistic studies of Sansalvamide A-amide: an allosteric modulator of Hsp90
- PMID: 20730035
- PMCID: PMC2922868
- DOI: 10.1021/ml900003t
Mechanistic studies of Sansalvamide A-amide: an allosteric modulator of Hsp90
Abstract
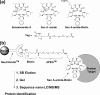
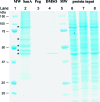
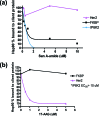
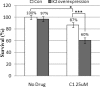
Herein we show that San A-amide, a structurally unique molecule, influences a subset of cancer-related pathways involving Hsp90. We show that San A-amide specifically binds to the N-middle domain of Hsp90 allosterically disrupts the binding of proteins thought to interact with the Hsp90 C-terminal domain, while having no effect on an N-terminal domain client protein. This unique mechanism suggests that San A-amide is a potential tool for studying C-terminal binding proteins of Hsp90 as well as a promising lead in the development of new cancer therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Hsp90 modulator that exhibits a unique mechanistic profile.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 May 1;22(9):3287-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Mar 11. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22480433 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of biotinylated sansalvamide A analogs and their modulation of Hsp90.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Aug 15;21(16):4716-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.083. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21764310 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Hsp90 C-terminal domain to induce allosteric inhibition and selective client downregulation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Aug;1861(8):1992-2006. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.006. Epub 2017 May 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28495207 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer Inhibitors of Hsp90 Function: Beyond the Usual Suspects.Adv Cancer Res. 2016;129:51-88. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.12.001. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Adv Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26916001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of small molecule Hsp90 inhibitors: utilizing both forward and reverse chemical genomics for drug identification.Curr Med Chem. 2003 May;10(9):733-9. doi: 10.2174/0929867033457818. Curr Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12678776 Review.
Cited by
-
Delivering bioactive cyclic peptides that target Hsp90 as prodrugs.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):728-739. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1580276. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30822267 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically accessible hsp90 inhibitor that does not induce a heat shock response.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014 May 13;5(7):771-6. doi: 10.1021/ml500114p. eCollection 2014 Jul 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 25050163 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved arginine 380 of Hsp90 is not a catalytic residue, but stabilizes the closed conformation required for ATP hydrolysis.Protein Sci. 2012 Aug;21(8):1162-71. doi: 10.1002/pro.2103. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22653663 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the Plasmodium falciparum Hsp90 towards Selective Antimalarial Drug Design: The Past, Present and Future.Cells. 2021 Oct 22;10(11):2849. doi: 10.3390/cells10112849. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A silicon-containing aryl/penta-1,4-dien-3-one/amine hybrid exhibits antiproliferative effects on breast cancer cells by targeting the HSP90 C-terminus without inducing heat-shock response.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Oct 23;14(12):2625-2639. doi: 10.1039/d3md00431g. eCollection 2023 Dec 13. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 38107168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cueto M.; Jensen P. R.; Fenical W. N-Methylsansalvamide, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 223–226. - PubMed
-
- Belofsky G. N.; Jensen P. R.; Fenical W. Sansalvamide: A new cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide produced by a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2913–2916.
-
- Hwang Y.; Rowley D.; Rhodes D.; Gertsch J.; Fenical W.; Bushman F. Mechanism of Inhibition of a Poxvirus Topoisomerase by the Marine Natural Product Sansalvamide A. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 55, 1049–1053. - PubMed
-
- Otrubova K.; Lushington G. H.; Vander Velde D.; McGuire K. L.; McAlpine S. R. A Comprehensive Study of Sansalvamide A Derivatives and Their Structure-Activity Relationships against Drug-Resistant Colon Cancer Cell Lines. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 530–544. - PubMed
-
- Pan P. S.; Vasko R. C.; Lapera S. A.; Johnson V. A.; Sellers R. P.; Lin C.-C.; Pan C.-M.; Davis M. R.; Ardi V. C.; McAlpine S. R. A comprehensive study of Sansalvamide A derivatives: Their structure-activity relationships and their binding mode to Hsp90. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5806–5825. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

