Mutations in the WTX-gene are found in some high-grade microsatellite instable (MSI-H) colorectal cancers
- PMID: 20696052
- PMCID: PMC2928794
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-413
Mutations in the WTX-gene are found in some high-grade microsatellite instable (MSI-H) colorectal cancers
Abstract
Background: Genetically, colorectal cancers (CRCs) can be subdivided into tumors with chromosomal instability (CIN) or microsatellite instability (MSI). In both types of CRCs genes that are involved in the degradation of beta-CATENIN are frequently mutated. Whereas in CIN CRCs APC (Adenomatous Polyposis Coli) is affected in most cases, high grade MSI (MSI-H) CRCs frequently display mutations in various genes, like the APC-, AXIN2- or CTNNBI (beta-CATENIN) gene itself. Recently in Wilms tumors, WTX (Wilms tumor gene on the X-chromosome) was discovered as another gene involved in the destruction of beta-CATENIN. As the WTX-gene harbors a short T6-microsatellite in its N-terminal coding region, we hypothesized that frameshift-mutations might occur in MSI-H CRCs in the WTX gene, thus additionally contributing to the stabilization of beta-CATENIN in human CRCs.
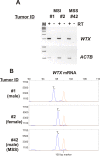
Methods: DNA was extracted from 632 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded metastatic CRCs (UICCIV) and analyzed for MSI-H by investigating the stability of the highly sensitive microsatellite markers BAT25 and BAT26 applying fluorescence capillary electrophoresis (FCE). Then, in the MSI-H cases, well described mutational hot spot regions from the APC-, AXIN2- and CTNNBI genes were analyzed for genomic alterations by didesoxy-sequencing while the WTX T6-microsatellite was analyzed by fragment analysis. Additionally, the PCR products of T5-repeats were subcloned and mutations were validated using didesoxy-sequencing. Furthermore, the KRAS and the BRAF proto-oncogenes were analyzed for the most common activating mutations applying pyro-sequencing. mRNA expression of WTX from MSI-H and MSS cases and a panel of colorectal cancer cell lines was investigated using reverse transcription (RT-) PCR and FCE.
Results: In our cohort of 632 metastatic CRCs (UICCIV) we identified 41 MSI-H cases (6.5%). Two of the 41 MSI-H cases (4.8%) displayed a frameshift mutation in the T6-repeat resulting in a T5 sequence. Only one case, a male patient, expressed the mutated WTX gene while being wild type for all other investigated genes.
Conclusion: Mutations in the WTX-gene might compromise the function of the beta-CATENIN destruction complex in only a small fraction of MSI-H CRCs thus contributing to the process of carcinogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutational profiling of colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):42334-44. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5997. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26517354 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Heterogeneity of Frameshift Mutations in MECOM Gene is Frequent in Colorectal Cancers with High Microsatellite Instability.Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Jan;23(1):145-149. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0112-3. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27620344
-
Microsatellite instability-low colorectal cancer acquires a KRAS mutation during the progression from Dukes' A to Dukes' B.Carcinogenesis. 2009 Mar;30(3):494-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp017. Epub 2009 Jan 15. Carcinogenesis. 2009. PMID: 19147861
-
Molecular and prognostic heterogeneity of microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4230-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4230. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Prognostic marker profiles for risk of distant metastases in colorectal cancer].Pathologe. 2012 Feb;33(1):39-44. doi: 10.1007/s00292-011-1543-y. Pathologe. 2012. PMID: 22293788 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Mir20a/106a-WTX axis regulates RhoGDIa/CDC42 signaling and colon cancer progression.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 10;10(1):112. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07998-x. Nat Commun. 2019. Retraction in: Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 18;14(1):5772. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41612-z. PMID: 30631060 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
BRCA2, EGFR, and NTRK mutations in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancers with MSH2 or MLH1 mutations.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):39945-39962. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18098. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28591715 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Cancer Phytometabolites Targeting Cancer Stem Cells.Curr Genomics. 2017 Apr;18(2):156-174. doi: 10.2174/1389202917666160803162309. Curr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28367074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The General Expression Analysis of WTX Gene in Normal and Cancer Tissues.Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Apr;23(2):439-446. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0168-0. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 28032309
-
Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.Nature. 2012 Jul 18;487(7407):330-7. doi: 10.1038/nature11252. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22810696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weisenberger DJ, Siegmund KD, Campan M, Young J, Long TI, Faasse MA, Kang GH, Widschwendter M, Weener D, Buchanan D. et al.CpG island methylator phenotype underlies sporadic microsatellite instability and is tightly associated with BRAF mutation in colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2006;38:787–793. doi: 10.1038/ng1834. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

