Inactivation and disassembly of the anaphase-promoting complex during human cytomegalovirus infection is associated with degradation of the APC5 and APC4 subunits and does not require UL97-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1
- PMID: 20686030
- PMCID: PMC2950577
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01260-10
Inactivation and disassembly of the anaphase-promoting complex during human cytomegalovirus infection is associated with degradation of the APC5 and APC4 subunits and does not require UL97-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1
Abstract
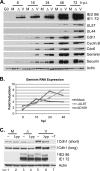
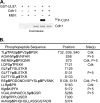
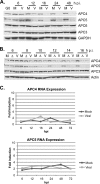
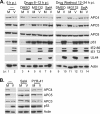
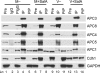
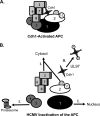
Infection of quiescent cells by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) elicits severe cell cycle deregulation, resulting in a G(1)/S arrest, which can be partly attributed to the inactivation of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC). As we previously reported, the premature phosphorylation of its coactivator Cdh1 and/or the dissociation of the core complex can account for the inactivation. We have expanded on these results and further delineated the key components required for disabling the APC during HCMV infection. The viral protein kinase UL97 was hypothesized to phosphorylate Cdh1, and consistent with this, phosphatase assays utilizing a virus with a UL97 deletion mutation (ΔUL97 virus) indicated that Cdh1 is hypophosphorylated at early times in the infection. Mass spectrometry analysis demonstrated that UL97 can phosphorylate Cdh1 in vitro, and the majority of the sites identified correlated with previously characterized cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) consensus sites. Analysis of the APC core complex during ΔUL97 virus infection showed APC dissociation occurring at the same time as during infection with wild-type virus, suggesting that the UL97-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1 is not required for this to occur. Further investigation of the APC subunits showed a proteasome-dependent loss of the APC5 and APC4 subunits that was temporally associated with the disassembly of the APC. Immediate early viral gene expression was not sufficient for the degradation of APC4 and APC5, indicating that a viral early gene product(s), possibly in association with a de novo-synthesized cellular protein(s), is involved.
Figures
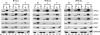


Similar articles
-
Studies on the Contribution of Human Cytomegalovirus UL21a and UL97 to Viral Growth and Inactivation of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C) E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Reveal a Unique Cellular Mechanism for Downmodulation of the APC/C Subunits APC1, APC4, and APC5.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6928-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00403-15. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25903336 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome-dependent disruption of the E3 ubiquitin ligase anaphase-promoting complex by HCMV protein pUL21a.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(7):e1002789. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002789. Epub 2012 Jul 5. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22792066 Free PMC article.
-
TPR subunits of the anaphase-promoting complex mediate binding to the activator protein CDH1.Curr Biol. 2003 Sep 2;13(17):1459-68. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00581-5. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12956947
-
Non-mitotic functions of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):572-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21439391 Review.
-
The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):579-85. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21497201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ULb' region of the human cytomegalovirus genome confers an increased requirement for the viral protein kinase UL97.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6359-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03477-12. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536674 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative temporal viromics: an approach to investigate host-pathogen interaction.Cell. 2014 Jun 5;157(6):1460-1472. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.028. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24906157 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic Profiling Reveals Epstein-Barr Virus Protein Kinase Integration of DNA Damage Response and Mitotic Signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Dec 29;11(12):e1005346. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005346. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26714015 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0396-z. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25776080 Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE1 protein disrupts interleukin-6 signaling by sequestering STAT3 in the nucleus.J Virol. 2013 Oct;87(19):10763-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01197-13. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23903834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht, T., M. P. Fons, I. Boldogh, S. AbuBakar, C. Z. Deng, and D. Millinoff. 1991. Metabolic and cellular effects of human cytomegalovirus infection. Transplant. Proc. 23:48-55. - PubMed
-
- Azzeh, M., A. Honigman, A. Taraboulos, A. Rouvinski, and D. Wolf. 2006. Structural changes in human cytomegalovirus cytoplasmic assembly sites in the absence of UL97 kinase activity. Virology 354:69-79. - PubMed
-
- Baek, M.-C., P. M. Krosky, Z. He, and D. M. Coen. 2002. Specific phosphorylation of exogenous protein and peptide substrates by the human cytomegalovirus UL97 protein kinase. Importance of the P+5 position. J. Biol. Chem. 277:29593-29599. - PubMed
-
- Baek, M.-C., P. M. Krosky, A. Pearson, and D. M. Coen. 2004. Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells and in vitro by the viral UL97 protein kinase. Virology 324:184-193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

