Notch regulates the switch from symmetric to asymmetric neural stem cell division in the Drosophila optic lobe
- PMID: 20685734
- PMCID: PMC2926952
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.051250
Notch regulates the switch from symmetric to asymmetric neural stem cell division in the Drosophila optic lobe
Abstract
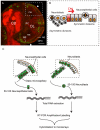
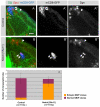
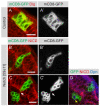
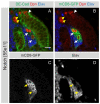
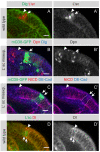
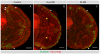
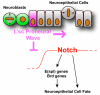
The proper balance between symmetric and asymmetric stem cell division is crucial both to maintain a population of stem cells and to prevent tumorous overgrowth. Neural stem cells in the Drosophila optic lobe originate within a polarised neuroepithelium, where they divide symmetrically. Neuroepithelial cells are transformed into asymmetrically dividing neuroblasts in a precisely regulated fashion. This cell fate transition is highly reminiscent of the switch from neuroepithelial cells to radial glial cells in the developing mammalian cerebral cortex. To identify the molecules that mediate the transition, we microdissected neuroepithelial cells and compared their transcriptional profile with similarly obtained optic lobe neuroblasts. We find genes encoding members of the Notch pathway expressed in neuroepithelial cells. We show that Notch mutant clones are extruded from the neuroepithelium and undergo premature neurogenesis. A wave of proneural gene expression is thought to regulate the timing of the transition from neuroepithelium to neuroblast. We show that the proneural wave transiently suppresses Notch activity in neuroepithelial cells, and that inhibition of Notch triggers the switch from symmetric, proliferative division, to asymmetric, differentiative division.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulating the balance between symmetric and asymmetric stem cell division in the developing brain.Fly (Austin). 2011 Jul-Sep;5(3):237-41. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.3.15640. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21502820 Review.
-
Drosophila medulla neuroblast termination via apoptosis, differentiation, and gliogenic switch is scheduled by the depletion of the neuroepithelial stem cell pool.Elife. 2024 Jun 21;13:e96876. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96876. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38905123 Free PMC article.
-
A Serrate-Notch-Canoe complex mediates essential interactions between glia and neuroepithelial cells during Drosophila optic lobe development.J Cell Sci. 2013 Nov 1;126(Pt 21):4873-84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.125617. Epub 2013 Aug 22. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23970418
-
Coordinated sequential action of EGFR and Notch signaling pathways regulates proneural wave progression in the Drosophila optic lobe.Development. 2010 Oct;137(19):3193-203. doi: 10.1242/dev.048058. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Development. 2010. PMID: 20724446
-
A challenge of numbers and diversity: neurogenesis in the Drosophila optic lobe.J Neurogenet. 2014 Sep-Dec;28(3-4):233-49. doi: 10.3109/01677063.2014.922558. Epub 2014 Jul 8. J Neurogenet. 2014. PMID: 24912777 Review.
Cited by
-
Protection of neuronal diversity at the expense of neuronal numbers during nutrient restriction in the Drosophila visual system.Cell Rep. 2013 Mar 28;3(3):587-94. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23478023 Free PMC article.
-
Cephalopod retinal development shows vertebrate-like mechanisms of neurogenesis.Curr Biol. 2022 Dec 5;32(23):5045-5056.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.10.027. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 36356573 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping neural progenitor cells on a short leash during Drosophila neurogenesis.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011 Feb;21(1):36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.09.005. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 20952184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular trafficking in Drosophila visual system development: a basis for pattern formation through simple mechanisms.Dev Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;71(12):1227-45. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20940. Dev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21714102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Drosophila intestinal stem cell maintenance and differentiation by the transcription factor Escargot.EMBO J. 2014 Dec 17;33(24):2983-96. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489050. Epub 2014 Nov 27. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25433031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida M. S., Bray S. J. (2005). Regulation of post-embryonic neuroblasts by Drosophila Grainyhead. Mech. Dev. 122, 1282-1293 - PubMed
-
- Bardin A. J., Schweisguth F. (2006). Bearded family members inhibit Neuralized-mediated endocytosis and signaling activity of Delta in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 10, 245-255 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand N., Castro D. S., Guillemot F. (2002). Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 517-530 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

