BRCT domain interactions with phospho-histone H2A target Crb2 to chromatin at double-strand breaks and maintain the DNA damage checkpoint
- PMID: 20679485
- PMCID: PMC2950532
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00413-10
BRCT domain interactions with phospho-histone H2A target Crb2 to chromatin at double-strand breaks and maintain the DNA damage checkpoint
Abstract
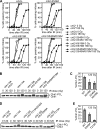
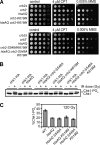
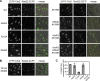
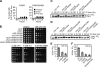
Relocalization of checkpoint proteins to chromatin flanking DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is critical for cellular responses to DNA damage. Schizosaccharomyces pombe Crb2, which mediates Chk1 activation by Rad3(ATR), forms ionizing radiation-induced nuclear foci (IRIF). Crb2 C-terminal BRCT domains (BRCT(2)) bind histone H2A phosphorylated at a C-terminal SQ motif by Tel1(ATM) and Rad3(ATR), although the functional significance of this interaction is controversial. Here, we show that polar interactions of Crb2 serine-548 and lysine-619 with the phosphate group of phospho-H2A (γ-H2A) are critical for Crb2 IRIF formation and checkpoint function. Mutations of these BRCT(2) domain residues have additive effects when combined in a single allele. Combining either mutation with an allele that eliminates the threonine-215 cyclin-dependent kinase phosphorylation site completely abrogates Crb2 IRIF and function. We propose that cooperative phosphate interactions in the BRCT(2) γ-H2A-binding pocket of Crb2, coupled with tudor domain interactions with lysine-20 dimethylation of histone H4, facilitate stable recruitment of Crb2 to chromatin surrounding DSBs, which in turn mediates efficient phosphorylation of Chk1 that is required for a sustained checkpoint response. This mechanism of cooperative interactions with the γ-H2A/X phosphate is likely conserved in S. pombe Brc1 and human Mdc1 genome maintenance proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Requirement for the phospho-H2AX binding module of Crb2 in double-strand break targeting and checkpoint activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(19):4722-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00404-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20679488 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H2A phosphorylation controls Crb2 recruitment at DNA breaks, maintains checkpoint arrest, and influences DNA repair in fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(14):6215-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6215-6230.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226425 Free PMC article.
-
Histone modification-dependent and -independent pathways for recruitment of checkpoint protein Crb2 to double-strand breaks.Genes Dev. 2006 Jun 15;20(12):1583-96. doi: 10.1101/gad.1422606. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16778077 Free PMC article.
-
Brc1 links replication stress response and centromere function.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jun 1;12(11):1665-71. doi: 10.4161/cc.24900. Epub 2013 May 8. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23656778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of and recovery from damage checkpoint requires sequential interactions of Crb2 with protein kinases Rad3, Chk1, and Cdc2.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2000;65:443-9. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2000.65.443. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2000. PMID: 12760060 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Requirement for the phospho-H2AX binding module of Crb2 in double-strand break targeting and checkpoint activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(19):4722-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00404-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20679488 Free PMC article.
-
Livin Regulates H2A.XY142 Phosphorylation and Promotes Autophagy in Colon Cancer Cells via a Novel Kinase Activity.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 14;9:1233. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01233. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31799193 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple DNA repair pathways contribute to MMS-induced post-replicative DNA synthesis in S. pombe.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Oct 2;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000974. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000974. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37854101 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-BRCT Domain Protein Brc1 Links Rhp18/Rad18 and γH2A To Maintain Genome Stability during S Phase.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Oct 27;37(22):e00260-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00260-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28784724 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Function of γH2A in S-Phase.PLoS Genet. 2015 Sep 14;11(9):e1005517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005517. eCollection 2015 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26368543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Downs, J. A., S. Allard, O. Jobin-Robitaille, A. Javaheri, A. Auger, N. Bouchard, S. J. Kron, S. P. Jackson, and J. Cote. 2004. Binding of chromatin-modifying activities to phosphorylated histone H2A at DNA damage sites. Mol. Cell 16:979-990. - PubMed
-
- Downs, J. A., N. F. Lowndes, and S. P. Jackson. 2000. A role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone H2A in DNA repair. Nature 408:1001-1004. - PubMed
-
- Du, L. L., B. A. Moser, and P. Russell. 2004. Homo-oligomerization is the essential function of the tandem BRCT domains in the checkpoint protein Crb2. J. Biol. Chem. 279:38409-38414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
