Regulation of ERalpha-mediated transcription of Bcl-2 by PI3K-AKT crosstalk: implications for breast cancer cell survival
- PMID: 20664923
- PMCID: PMC3613138
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo_00000703
Regulation of ERalpha-mediated transcription of Bcl-2 by PI3K-AKT crosstalk: implications for breast cancer cell survival
Abstract
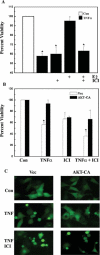
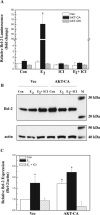
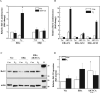
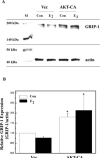
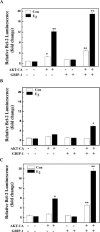
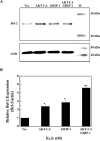
Both estrogen, through the estrogen receptor (ER), and growth factors, through the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT pathway, have been shown to independently promote cell survival. Here, we investigated the role of ER/PI3K-AKT crosstalk in the regulation of cell survival in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. The ER inhibitor ICI 182,780 was used to determine the requirement of the ER for estrogen in the suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) induced apoptosis. Gene reporter assays and Western blot analyses were used to determine the involvement of the pro-survival factor Bcl-2 and the coactivator GRIP1 in this survival crosstalk. We demonstrated that an intact ER signaling pathway was required for estrogen to suppress apoptosis induced by TNFalpha. Our gene reporter assays revealed that ERalpha, not ERbeta, was targeted by AKT, resulting in transcriptional potentiation of the full-length Bcl-2 promoter, ultimately leading to increased Bcl-2 protein levels. AKT targeted both activation function (AF) domains of the ERalpha for maximal induction of Bcl-2 reporter activity, although the AF-II domain was predominately targeted. In addition, AKT also caused an upregulation of GRIP1 protein levels. Finally, AKT and GRIP1 cooperated to increase Bcl-2 protein expression to a greater level than either factor alone. Collectively, our study suggests a role for ER/PI3K-AKT crosstalk in cell survival and documents the ability of AKT to regulate Bcl-2 expression via differential activation of ERalpha and ERbeta as well as regulation of GRIP1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) regulates estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-alpha) expression and cell apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway in human breast cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2009 Aug;29(8):3195-205. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19661335
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 30;276(13):9817-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010840200. Epub 2001 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11139588
-
Obesity enhances nongenomic estrogen receptor crosstalk with the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways to promote in vitro measures of breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R59. doi: 10.1186/bcr3453. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23880059 Free PMC article.
-
Nexus between PI3K/AKT and Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 20;13(3):369. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030369. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormonal regulation of metabolism-recent lessons learned from insulin and estrogen.Clin Sci (Lond). 2023 Mar 31;137(6):415-434. doi: 10.1042/CS20210519. Clin Sci (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36942499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing GTSE-1 expression inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016 Aug;32(4):263-74. doi: 10.1007/s10565-016-9327-z. Epub 2016 May 30. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27240802 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Neuroglobin as a Stress-Induced Factor Activating Pre-Adaptation Mechanisms against Oxidative Stress and Chemotherapy-Induced Cell Death in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 29;12(9):2451. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092451. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872414 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of luteal transcriptome during prostaglandin F2-alpha treatment in buffalo cows: analysis of signaling pathways associated with luteolysis.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 7;9(8):e104127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104127. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25102061 Free PMC article.
-
The scaffold protein MEK Partner 1 is required for the survival of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2012 Jul 9;10(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-18. Cell Commun Signal. 2012. PMID: 22776333 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Glomerular Protein Expression and Effects of Soy-Based Diet on Podocyte Signaling.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2022 Sep 30;9:20543581221121636. doi: 10.1177/20543581221121636. eCollection 2022. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36199279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar R, Vadlamudi RK, Adam L. Apoptosis in mammary gland and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2000;7:257–269. - PubMed
-
- Green DR, Evan GI. A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:19–30. - PubMed
-
- Imagawa W, Pedchenko VK, Helber J, Zhang H. Hormone/growth factor interactions mediating epithelial/stromal communication in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;80:213–230. - PubMed
-
- Feigelson HS, Henderson BE. Estrogens and breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1996;17:2279–2284. - PubMed
-
- Gross JM, Yee D. The type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: Biology and therapeutic relevance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:327–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

