A phosphatidic acid binding/nuclear localization motif determines lipin1 function in lipid metabolism and adipogenesis
- PMID: 20660155
- PMCID: PMC2938383
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0073
A phosphatidic acid binding/nuclear localization motif determines lipin1 function in lipid metabolism and adipogenesis
Abstract
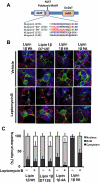
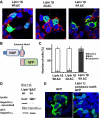
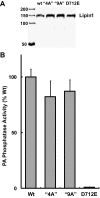
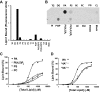
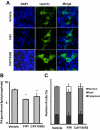
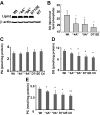
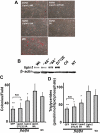
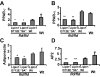
Lipins are phosphatidic acid phosphatases with a pivotal role in regulation of triglyceride and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Lipin1 is also an amplifier of PGC-1α, a nuclear coactivator of PPAR-α responsive gene transcription. Lipins do not contain recognized membrane-association domains, but interaction of these enzymes with cellular membranes is necessary for access to their phospholipid substrate. We identified a role for a conserved polybasic amino acid motif in an N-terminal domain previously implicated as a determinant of nuclear localization in selective binding of lipin1β to phosphatidic acid, using blot overlay assays and model bilayer membranes. Studies using lipin1β polybasic motif variants establish that this region is also critical for nuclear import and raise the possibility that nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling of lipin1β is regulated by PA. We used pharmacological agents and lipin1β polybasic motif mutants to explore the role of PA-mediated membrane association and nuclear localization on lipin1β function in phospholipid metabolism and adipogenic differentiation. We identify a role for the lipin1 polybasic motif as both a lipid binding motif and a primary nuclear localization sequence. These two functions are necessary for full expression of the biological activity of the protein in intracellular lipid metabolism and transcriptional control of adipogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The phosphatidic acid-binding, polybasic domain is responsible for the differences in the phosphoregulation of lipins 1 and 3.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 15;292(50):20481-20493. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.786574. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28982975 Free PMC article.
-
Lipin-1 phosphatidic phosphatase activity modulates phosphatidate levels to promote peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) gene expression during adipogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 27;287(5):3485-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.296681. Epub 2011 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22157014 Free PMC article.
-
The importin-alpha/nucleophosmin switch controls taspase1 protease function.Traffic. 2011 Jun;12(6):703-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01191.x. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21418451
-
Phospholipid metabolism and nuclear function: roles of the lipin family of phosphatidic acid phosphatases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):575-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.09.014. Epub 2012 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23026159 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of lipin inhibitors for the treatment of cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;222:116106. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116106. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38442792 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-203 Inhibits Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Targeting Lipin1.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 4;9:275. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00275. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29670525 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the Spo20 membrane-sensor motif with phosphatidic acid and other anionic lipids, and influence of the membrane environment.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e113484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113484. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25426975 Free PMC article.
-
The middle lipin domain adopts a membrane-binding dimeric protein fold.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 5;12(1):4718. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24929-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34354069 Free PMC article.
-
PLD1 regulates adipogenic differentiation through mTOR - IRS-1 phosphorylation at serine 636/639.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 22;6:36968. doi: 10.1038/srep36968. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27872488 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction and Regulation Between Lipid Mediator Phosphatidic Acid and Circadian Clock Regulators.Plant Cell. 2019 Feb;31(2):399-416. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00675. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 30674693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bou Khalil M., Sundaram M., Zhang H. Y., Links P. H., Raven J. F., Manmontri B., Sariahmetoglu M., Tran K., Reue K., Brindley D. N., Yao Z. The level and compartmentalization of phosphatidate phosphatase-1 (lipin-1) control the assembly and secretion of hepatic VLDL. J. Lipid Res. 2009;50:47–58. - PubMed
-
- Buser C. A., McLaughlin S. Ultracentrifugation technique for measuring the binding of peptides and proteins to sucrose-loaded phospholipid vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 1998;84:267–281. - PubMed
-
- Donkor J., Sariahmetoglu M., Dewald J., Brindley D. N., Reue K. Three mammalian lipins act as phosphatidate phosphatases with distinct tissue expression patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:3450–3457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

