Widespread genomic breaks generated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase are prevented by homologous recombination
- PMID: 20657597
- PMCID: PMC2930818
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1909
Widespread genomic breaks generated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase are prevented by homologous recombination
Abstract
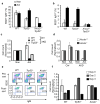
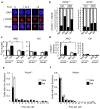
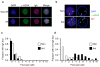
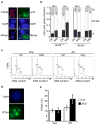
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is required for somatic hypermutation and immunoglobulin class switching in activated B cells. Because AID has no known target-site specificity, there have been efforts to identify non-immunoglobulin AID targets. We show here that AID acts promiscuously, generating widespread DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), genomic instability and cytotoxicity in B cells with less homologous recombination ability. We demonstrate that the homologous-recombination factor XRCC2 suppressed AID-induced off-target DSBs, promoting B cell survival. Finally, we suggest that aberrations that affect human chromosome 7q36, including XRCC2, correlate with genomic instability in B cell cancers. Our findings demonstrate that AID has promiscuous genomic DSB-inducing activity, identify homologous recombination as a safeguard against off-target AID action, and have implications for genomic instability in B cell cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase-initiated off-target DNA breaks are detected and resolved during S phase.J Immunol. 2012 Sep 1;189(5):2374-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200414. Epub 2012 Jul 23. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22826323 Free PMC article.
-
AID- and Ung-dependent generation of staggered double-strand DNA breaks in immunoglobulin class switch DNA recombination: a post-cleavage role for AID.Mol Immunol. 2008 Nov;46(1):45-61. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18760480 Free PMC article.
-
AID-associated DNA repair pathways regulate malignant transformation in a murine model of BCL6-driven diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2016 Jan 7;127(1):102-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-628164. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26385350 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing AID, a physiological mutator, from deleterious activation: regulation of the genomic instability that is associated with antibody diversity.Int Immunol. 2010 Apr;22(4):227-35. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq023. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20207715 Review.
-
Immunoglobulin somatic hypermutation: double-strand DNA breaks, AID and error-prone DNA repair.J Clin Immunol. 2003 Jul;23(4):235-46. doi: 10.1023/a:1024571714867. J Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12959216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Personalized synthetic lethality induced by targeting RAD52 in leukemias identified by gene mutation and expression profile.Blood. 2013 Aug 15;122(7):1293-304. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-501072. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23836560 Free PMC article.
-
The AID-induced DNA damage response in chromatin.Mol Cell. 2013 May 9;50(3):309-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.017. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23664375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulation and function of activation-induced cytidine deaminase.Trends Immunol. 2011 May;32(5):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.03.003. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Trends Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21493144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etoposide induces nuclear re-localisation of AID.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 4;8(12):e82110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082110. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24324754 Free PMC article.
-
BCR and Endosomal TLR Signals Synergize to Increase AID Expression and Establish Central B Cell Tolerance.Cell Rep. 2017 Feb 14;18(7):1627-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.050. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28199836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mills KD, Ferguson DO, Alt FW. The role of DNA breaks in genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Immunol Rev. 2003;194:77–95. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu M, Nagaoka H, Shinkura R, Begum NA, Honjo T. Discovery of activation-induced cytidine deaminase, the engraver of antibody memory. Adv Immunol. 2007;94:1–36. - PubMed
-
- Durandy A, Taubenheim N, Peron S, Fischer A. Pathophysiology of B-cell intrinsic immunoglobulin class switch recombination deficiencies. Adv Immunol. 2007;94:275–306. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri J, et al. Evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination mechanism. Adv Immunol. 2007;94:157–214. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, et al. Two levels of protection for the B cell genome during somatic hypermutation. Nature. 2008;451:841–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20RR018789-06/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007449/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196-26/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138646/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA138646/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK07449-26/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138646-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR018789/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR018789-076566/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007449-26/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

