Regulation of system x(c)(-)activity and expression in astrocytes by interleukin-1β: implications for hypoxic neuronal injury
- PMID: 20645408
- PMCID: PMC4451603
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.21050
Regulation of system x(c)(-)activity and expression in astrocytes by interleukin-1β: implications for hypoxic neuronal injury
Abstract
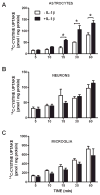
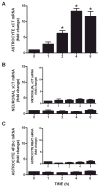
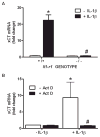
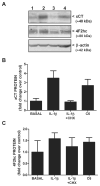
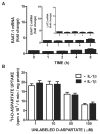
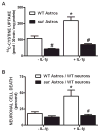
We recently demonstrated that interleukin-1β (IL-1β) increases system x(c)(-) (cystine/glutamate antiporter) activity in mixed cortical cell cultures, resulting in an increase in hypoxic neuronal injury when glutamate clearance is impaired. Herein, we demonstrate that neurons, astrocytes, and microglia all express system x(c)(-) subunits (xCT, 4F2hc, RBAT) and are capable of cystine import. However, IL-1β stimulation increases mRNA for xCT--the light chain that confers substrate specificity--in astrocytes only; an effect blocked by the transcriptional inhibitor actinomycin D. Additionally, only astrocytes show an increase in cystine uptake following IL-1β exposure; an effect associated with a change in xCT protein. The increase in cystine uptake that follows IL-1β is lacking in astrocytes derived from mice harboring a mutation in Slc7a11 (sut gene), which encodes for xCT, and in wild-type astrocytes treated with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. IL-1β does not regulate the light chain of the amino acid transporter, LAT2, or the expression and function of astrocytic excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs), demonstrating some target selectivity. Finally, the enhanced neuronal vulnerability to hypoxia that followed IL-1β treatment in our mixed culture system was not observed in chimeric cultures consisting of wild-type neurons plated on top of sut astrocytes. Nor was it observed in wild-type cultures treated with a system x(c)(-) inhibitor or an NMDA receptor antagonist. Overall, our data demonstrate that IL-1β selectively regulates system x(c)(-) activity in astrocytes and that this change is specifically responsible for the deleterious, excitotoxic effects of IL-1β found under hypoxic conditions.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
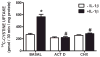
Similar articles
-
System x(c)- activity and astrocytes are necessary for interleukin-1 beta-mediated hypoxic neuronal injury.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 19;27(38):10094-105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2459-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17881516 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 1β Regulation of the System xc- Substrate-specific Subunit, xCT, in Primary Mouse Astrocytes Involves the RNA-binding Protein HuR.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1643-1651. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.697821. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26601945 Free PMC article.
-
Non-cell autonomous influence of the astrocyte system xc- on hypoglycaemic neuronal cell death.ASN Neuro. 2012 Feb 8;4(1):e00074. doi: 10.1042/AN20110030. ASN Neuro. 2012. PMID: 22220511 Free PMC article.
-
Glial Glutamate Transporter-Mediated Plasticity: System xc-/xCT/SLC7A11 and EAAT1/2 in Brain Diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 20;28(3):57. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2803057. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37005761 Review.
-
Mechanisms of oxidative glutamate toxicity: the glutamate/cystine antiporter system xc- as a neuroprotective drug target.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Jul;9(3):373-82. doi: 10.2174/187152710791292567. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20053169 Review.
Cited by
-
Main path and byways: non-vesicular glutamate release by system xc(-) as an important modifier of glutamatergic neurotransmission.J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(6):1062-79. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13348. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26336934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter, System xc -, Contributes to Cortical Infarction After Moderate but Not Severe Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 9;16:821036. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.821036. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35669109 Free PMC article.
-
The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Feb 10;18(5):522-55. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22667998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-1β induces rod degeneration through the disruption of retinal glutamate homeostasis.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 3;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1655-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31900165 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of System xc(-) by Pharmacological Manipulation of Cellular Thiols.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:269371. doi: 10.1155/2015/269371. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 25949770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backus KH, Kettenmann H, Schachner M. Pharmacological characterization of the glutamate receptor in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 1989;22(3):274–82. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Shen H, Kalivas PW. Cystine/glutamate exchange serves as the source for extracellular glutamate: modifications by repeated cocaine administration. Amino Acids. 2002a;23(1–3):161–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

