Native low-density lipoprotein uptake by macrophage colony-stimulating factor-differentiated human macrophages is mediated by macropinocytosis and micropinocytosis
- PMID: 20634472
- PMCID: PMC3170564
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.210849
Native low-density lipoprotein uptake by macrophage colony-stimulating factor-differentiated human macrophages is mediated by macropinocytosis and micropinocytosis
Abstract
Objective: To examine the pinocytotic pathways mediating native low-density lipoprotein (LDL) uptake by human macrophage colony-stimulating factor-differentiated macrophages (the predominant macrophage phenotype in human atherosclerotic plaques).
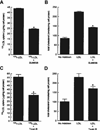
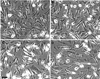
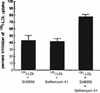
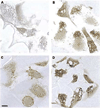
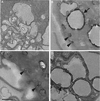
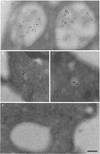
Methods and results: We identified the kinase inhibitor SU6656 and the Rho GTPase inhibitor toxin B as inhibitors of macrophage fluid-phase pinocytosis of LDL. Assessment of macropinocytosis by time-lapse microscopy revealed that both drugs almost completely inhibited macropinocytosis, although LDL uptake and cholesterol accumulation by macrophages were only partially inhibited (approximately 40%) by these agents. Therefore, we investigated the role of micropinocytosis in mediating LDL uptake in macrophages and identified bafilomycin A1 as an additional partial inhibitor (approximately 40%) of macrophage LDL uptake that targeted micropinocytosis. When macrophages were incubated with both bafilomycin A1 and SU6656, inhibition of LDL uptake was additive (reaching 80%), showing that these inhibitors target different pathways. Microscopic analysis of fluid-phase uptake pathways in these macrophages confirmed that LDL uptake occurs through both macropinocytosis and micropinocytosis.
Conclusions: Our findings show that human macrophage colony-stimulating factor-differentiated macrophages take up native LDL by macropinocytosis and micropinocytosis, underscoring the importance of both pathways in mediating LDL uptake by these cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluid-phase pinocytosis of native low density lipoprotein promotes murine M-CSF differentiated macrophage foam cell formation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58054. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058054. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536783 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid-phase pinocytosis of LDL by macrophages: a novel target to reduce macrophage cholesterol accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(33):5865-72. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319330005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23438954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive receptor-independent low density lipoprotein uptake and cholesterol accumulation by macrophages differentiated from human monocytes with macrophage-colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF).J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 9;281(23):15757-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510714200. Epub 2006 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16606620
-
Macropinocytosis is the endocytic pathway that mediates macrophage foam cell formation with native low density lipoprotein.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 21;280(3):2352-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407167200. Epub 2004 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15533943
-
Receptor-independent fluid-phase pinocytosis mechanisms for induction of foam cell formation with native low-density lipoprotein particles.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011 Oct;22(5):386-93. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32834adadb. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011. PMID: 21881499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of macropinocytosis in macrophages by cytokines: implications for foam cell formation and atherosclerosis.Cytokine. 2013 Oct;64(1):357-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23791479 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain-6 confers atherogenicity to macrophages by dysregulating pre-mRNA splicing.J Clin Invest. 2016 Sep 1;126(9):3417-32. doi: 10.1172/JCI85880. Epub 2016 Aug 15. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27525442 Free PMC article.
-
Akt3 kinase suppresses pinocytosis of low-density lipoprotein by macrophages via a novel WNK/SGK1/Cdc42 protein pathway.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 2;292(22):9283-9293. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773739. Epub 2017 Apr 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28389565 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired hemoglobin clearance by sinusoidal endothelium promotes vaso-occlusion and liver injury in sickle cell disease.Haematologica. 2024 May 1;109(5):1535-1550. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283792. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 37941440 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation is differentially regulated by high-density and low-density lipoproteins in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047286. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Hoff HF, Gaubatz JW, Gotto AM., Jr Apo B concentration in the normal human aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978;85:1424–1430. - PubMed
-
- Smith EB. Transport, interactions and retention of plasma proteins in the intima: the barrier function of the internal elastic lamina. Eur Heart J. 1990;11 suppl E:72–81. - PubMed
-
- Smith EB, Ashall C. Low-density lipoprotein concentration in interstitial fluid from human atherosclerotic lesions: relation to theories of endothelial damage and lipoprotein binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983;754:249–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

