Early growth response-1 attenuates liver injury and promotes hepatoprotection after carbon tetrachloride exposure in mice
- PMID: 20615570
- PMCID: PMC2930032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.04.017
Early growth response-1 attenuates liver injury and promotes hepatoprotection after carbon tetrachloride exposure in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Inflammatory gene expression plays a pathological role in acute and chronic hepatic inflammation, yet, inflammation also promotes liver repair by inducing protective mechanisms to limit collateral tissue damage by priming hepatocytes for proliferation. Early growth response (Egr)-1, a transcription factor that regulates inflammatory gene expression, plays a pathological role in many animal models of acute and chronic inflammatory disease. Here, we tested the hypothesis that Egr-1 is beneficial after toxic liver injury.
Methods: Acute liver injury was induced in wild-type and egr-1-/- mice by a single injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)). Liver injury, inflammatory, and hepatoprotective gene expression and signaling events were measured 18, 48, and 72 h after CCl(4) administration.
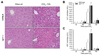
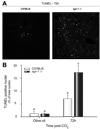
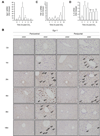
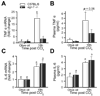
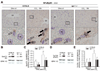
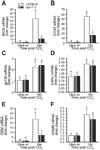
Results: Peak liver injury was greater in egr-1-/- mice compared to wild-type mice. Enhanced injury in egr-1-/- mice was associated with reduced tumor necrosis factor (TNF)alpha mRNA and protein expression, reduced Akt phosphorylation and nuclear localization of NFkappaB-p65 in nuclei of cells in the hepatic sinusoid. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2, TNFalpha-regulated genes that have hepatoprotective function, was attenuated in egr-1-/- mice compared to wild-type mice. Although plasma interleukin (IL)-6 protein and hepatic accumulation of IL-6, glycoprotein 130, and IL-6 receptor alpha mRNA in wild-type and egr-1-/- mice were equivalent, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation was attenuated in egr-1-/- mice and associated with reduced oncostatin M expression.
Conclusions: In contrast to its role in inflammation-mediated tissue injury in other models, Egr-1 expression promotes protection in the liver after CCl(4) exposure.
Copyright © 2010 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early growth response (EGR)-1 is required for timely cell-cycle entry and progression in hepatocytes after acute carbon tetrachloride exposure in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Jun;300(6):G1124-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00544.2010. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21415413 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response-1 contributes to galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):G1124-33. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00325.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17916644
-
Hepatic fibrosis is enhanced and accompanied by robust oval cell activation after chronic carbon tetrachloride administration to Egr-1-deficient mice.Am J Pathol. 2010 Jun;176(6):2743-52. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.091186. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20395449 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-induced liver injury: potential roles for egr-1.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):146S-150S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189286.81943.51. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16344600 Review.
-
Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):583-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23567086 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression analysis of inflammasomes in experimental models of inflammatory and fibrotic liver disease.J Inflamm (Lond). 2012 Nov 28;9(1):49. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-9-49. J Inflamm (Lond). 2012. PMID: 23192004 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to ethanol-induced liver injury by mediating cell injury, steatohepatitis, and steatosis.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1980-91. doi: 10.1002/hep.26169. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23174952 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical exacerbation of neuronal injury in reperfused stroke despite improved blood flow and reduced inflammation in early growth response-1 gene-deleted mice.Neurol Res. 2011 Sep;33(7):717-25. doi: 10.1179/1743132810Y.0000000022. Neurol Res. 2011. PMID: 21756551 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate (2%, v/v) Ethanol Feeding Alters Hepatic Wound Healing after Acute Carbon Tetrachloride Exposure in Mice.Biomolecules. 2016 Jan 6;6(1):5. doi: 10.3390/biom6010005. Biomolecules. 2016. PMID: 26751492 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 protection against liver injury produced by various hepatotoxicants.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:305861. doi: 10.1155/2013/305861. Epub 2013 May 23. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23766851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhave VS, Donthamsetty S, Latendresse JR, Mehendale HM. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 aggravates secretory phospholipase A2-mediated progression of acute liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 15;228(2):239–246. - PubMed
-
- Bhave VS, Donthamsetty S, Latendresse JR, Muskhelishvili L, Mehendale HM. Secretory phospholipase A2 mediates progression of acute liver injury in the absence of sufficient cyclooxygenase-2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 15;228(2):225–238. - PubMed
-
- Fausto N, Campbell JS, Riehle KJ. Liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2006 Feb;43(2) Suppl 1:S45–S53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

