Alpha/beta interferon (IFN-alpha/beta)-independent induction of IFN-lambda1 (interleukin-29) in response to Hantaan virus infection
- PMID: 20592090
- PMCID: PMC2937636
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00717-10
Alpha/beta interferon (IFN-alpha/beta)-independent induction of IFN-lambda1 (interleukin-29) in response to Hantaan virus infection
Abstract
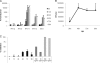
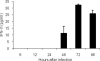
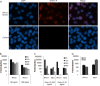
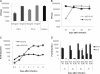
Type III interferons ([IFNs] IFN-lambda and interleukin-28 and -29 [IL-28/29]) are recently recognized cytokines with innate antiviral effects similar to those of type I IFNs (IFN-alpha/beta). Like IFN-alpha/beta, IFN-lambda-expression can be induced by viruses, and it is believed that type I and III IFNs are regulated in the same manner. Hantaviruses are weak IFN-alpha/beta inducers and have surprisingly been shown to activate IFN-alpha/beta-independent IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) expression. Here, we show that in Hantaan virus (HTNV)-infected human epithelial A549 cells, induction of IFN-lambda1 preceded induction of MxA and IFN-beta by 12 and 24 h, respectively, and IFN-alpha was not induced at all. Furthermore, induction of IFN-lambda1 and MxA was observed in HTNV-infected African green monkey epithelial Vero E6 cells, a cell line that cannot produce type I IFNs, clearly showing that HTNV can induce IFN-lambda1 and ISGs in the complete absence of IFN-alpha/beta. In HTNV-infected human fibroblast MRC-5 cells, which lack the IFN-lambda receptor, induction of MxA coincided in time with IFN-beta-induction. UV-inactivated HTNV did not induce any IFNs or MxA in any cell line, showing that activation of IFN-lambda1 is dependent on replicating virus. Induction of both IFN-beta and IFN-lambda1 in A549 cells after poly(I:C)-stimulation was strongly inhibited in HTNV-infected cells, suggesting that HTNV can inhibit signaling pathways used to simultaneously activate types I and III IFNs. In conclusion, we show that HTNV can cause type I IFN-independent IFN-lambda1 induction and IFN-lambda1-specific ISG induction. Importantly, the results suggest the existence of specific signaling pathways that induce IFN-lambda1 without simultaneous type I IFN induction during virus infection.
Figures
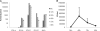
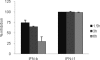
Similar articles
-
Hantaan virus triggers TLR3-dependent innate immune responses.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 1;182(5):2849-58. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802893. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19234180
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
Differential antiviral response of endothelial cells after infection with pathogenic and nonpathogenic hantaviruses.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6143-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6143-6150.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163707 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-λs.Curr Opin Immunol. 2011 Oct;23(5):583-90. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21840693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-lambda: a new addition to an old family.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010 Aug;30(8):555-64. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0078. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010. PMID: 20712453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine and chemokine responses of lung exposed to surrogate viral and bacterial infections.Comp Med. 2013 Apr;63(2):114-26. Comp Med. 2013. PMID: 23582418 Free PMC article.
-
HTNV infection induces activation and deficiency of CD8+MAIT cells in HFRS patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;211(1):1-14. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac111. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36480318 Free PMC article.
-
Incoming RNA virus nucleocapsids containing a 5'-triphosphorylated genome activate RIG-I and antiviral signaling.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Mar 13;13(3):336-46. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.01.012. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23498958 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon production and signaling pathways are antagonized during henipavirus infection of fruit bat cell lines.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022488. Epub 2011 Jul 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21811620 Free PMC article.
-
Puumala and Tula Virus Differ in Replication Kinetics and Innate Immune Stimulation in Human Endothelial Cells and Macrophages.Viruses. 2019 Sep 14;11(9):855. doi: 10.3390/v11090855. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31540120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ank, N., H. West, and S. R. Paludan. 2006. IFN-λ: novel antiviral cytokine. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 26:373-379. - PubMed
-
- Ank, N., M. B. Iversen, C. Bartholdy, P. Staeheli, R. Hartmann, U. B. Jensen, F. Dagnaes-Hansen, A. R. Thomsen, Z. Chen, H. Haugen, K. Klucher, and S. R. Paludan. 2008. An important role for type III interferon (IFN-lambda/IL-28) in TLR-induced antiviral activity. J. Immunol. 180:2474-2485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

