Pax6 controls the expression of critical genes involved in pancreatic {alpha} cell differentiation and function
- PMID: 20592023
- PMCID: PMC2963382
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.147215
Pax6 controls the expression of critical genes involved in pancreatic {alpha} cell differentiation and function
Abstract
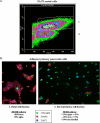
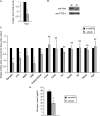
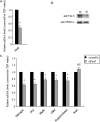
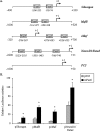
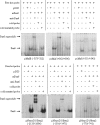
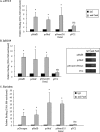
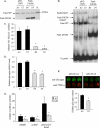
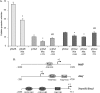
The paired box homeodomain Pax6 is crucial for endocrine cell development and function and plays an essential role in glucose homeostasis. Indeed, mutations of Pax6 are associated with diabetic phenotype. Importantly, homozygous mutant mice for Pax6 are characterized by markedly decreased β and δ cells and absent α cells. To better understand the critical role that Pax6 exerts in glucagon-producing cells, we developed a model of primary rat α cells. To study the transcriptional network of Pax6 in adult and differentiated α cells, we generated Pax6-deficient primary rat α cells and glucagon-producing cells, using either specific siRNA or cells expressing constitutively a dominant-negative form of Pax6. In primary rat α cells, we confirm that Pax6 controls the transcription of the Proglucagon and processing enzyme PC2 genes and identify three new target genes coding for MafB, cMaf, and NeuroD1/Beta2, which are all critical for Glucagon gene transcription and α cell differentiation. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Pax6 directly binds and activates the promoter region of the three genes through specific binding sites and that constitutive expression of a dominant-negative form of Pax6 in glucagon-producing cells (InR1G9) inhibits the activities of the promoters. Finally our results suggest that the critical role of Pax6 action on α cell differentiation is independent of those of Arx and Foxa2, two transcription factors that are necessary for α cell development. We conclude that Pax6 is critical for α cell function and differentiation through the transcriptional control of key genes involved in glucagon gene transcription, proglucagon processing, and α cell differentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucagon gene expression in the endocrine pancreas: the role of the transcription factor Pax6 in α-cell differentiation, glucagon biosynthesis and secretion.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Oct;13 Suppl 1:31-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01445.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21824254 Review.
-
Pax6 is crucial for β-cell function, insulin biosynthesis, and glucose-induced insulin secretion.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr;26(4):696-709. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1256. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22403172 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 regulates the proglucagon processing enzyme PC2 and its chaperone 7B2.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(8):2322-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01543-08. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19223471 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF mediates effect of insulin on glucagon expression.Exp Cell Res. 2012 May 1;318(8):887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Exp Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22426149 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty Years' History since the Discovery of Pax6: From Central Nervous System Development to Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 30;23(11):6115. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116115. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple functions of Maf in the regulation of cellular development and differentiation.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Nov;31(8):773-8. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2676. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 26122665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Long Noncoding RNA Paupar Modulates PAX6 Regulatory Activities to Promote Alpha Cell Development and Function.Cell Metab. 2019 Dec 3;30(6):1091-1106.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.013. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 31607563 Free PMC article.
-
High-fat diet consumption during pregnancy and the early post-natal period leads to decreased α cell plasticity in the nonhuman primate.Mol Metab. 2012 Nov 14;2(1):10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2012.11.001. eCollection 2012. Mol Metab. 2012. PMID: 24024126 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Pax6 is required for pancreatic β cell identity, glucose-regulated ATP synthesis, and Ca2+ dynamics in adult mice.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 26;292(21):8892-8906. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784629. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28377501 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental regulator Pax6 is essential for maintenance of islet cell function in the adult mouse pancreas.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054173. Epub 2013 Jan 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunning B. E., Gerich J. E. (2007) Endocr. Rev. 28, 253–283 - PubMed
-
- Sander M., Neubüser A., Kalamaras J., Ee H. C., Martin G. R., German M. S. (1997) Genes Dev. 11, 1662–1673 - PubMed
-
- St-Onge L., Sosa-Pineda B., Chowdhury K., Mansouri A., Gruss P. (1997) Nature 387, 406–409 - PubMed
-
- Lee C. S., Sund N. J., Behr R., Herrera P. L., Kaestner K. H. (2005) Dev. Biol. 278, 484–495 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

