NSAIDs: How they Work and their Prospects as Therapeutics in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 20589102
- PMCID: PMC2893374
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00020
NSAIDs: How they Work and their Prospects as Therapeutics in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
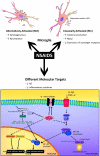
There is significant epidemiological evidence to suggest that there are beneficial effects of treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in Alzheimer's disease, although these effects have not been reproduced in clinical trials. The failure of the clinical trials may be attributed to several possible facts: (1) NSAIDS may have been delivered too late to patients, as they may only be effective in early stages of the disease and possibly counterproductive in the late stages; (2) the beneficial effect may depend on the drug, because different NSAIDs may have different molecular targets; (3) the NSAID concentration reaching the brain and the duration of the treatment could also be critical, so increasing drug penetration is important in order to improve the efficacy and avoid secondary gastro-intestinal effects of the NSAIDs. In this report we analyze these different factors, with special emphasis on the role of NSAIDs in microglia activation over time.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; NSAIDs; PPARγ; amyloid; microglia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Staging anti-inflammatory therapy in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2010 Oct 25;2:142. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00142. eCollection 2010. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21152343 Free PMC article.
-
[Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with selectivity for cyclooxygenase-2 in Alzheimer's disease. Rationale and perspectives].Presse Med. 2000 Feb 12;29(5):267-73. Presse Med. 2000. PMID: 10701410 Review. French.
-
[The possible suppression of Alzheimer's disease by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2002 Nov 2;146(44):2074-8. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2002. PMID: 12448960 Review. Dutch.
-
Soothing the inflamed brain: effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on Alzheimer's disease pathology.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;10(1):57-67. doi: 10.2174/187152711794488665. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21143138 Review.
-
From epidemiology to therapeutic trials with anti-inflammatory drugs in Alzheimer's disease: the role of NSAIDs and cyclooxygenase in beta-amyloidosis and clinical dementia.J Alzheimers Dis. 2002 Oct;4(5):435-45. doi: 10.3233/jad-2002-4510. J Alzheimers Dis. 2002. PMID: 12446975
Cited by
-
Evidence of endothelial dysfunction in the development of Alzheimer's disease: Is Alzheimer's a vascular disorder?Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2013 Nov 1;3(4):197-226. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 24224133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia function in Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 10;3:14. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00014. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22363284 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin: a natural substance with potential efficacy in Alzheimer's disease.J Exp Pharmacol. 2013 May 2;5:23-31. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S26803. eCollection 2013. J Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 27186134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Applications of NSAIDs: Insight and Future Perspectives in Cardiovascular, Neurodegenerative, Diabetes and Cancer Disease Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 21;22(12):6637. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126637. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34205719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarsasapogenin-AA13 ameliorates Aβ-induced cognitive deficits via improving neuroglial capacity on Aβ clearance and antiinflammation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Jun;23(6):498-509. doi: 10.1111/cns.12697. Epub 2017 May 3. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017. PMID: 28466999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alafuzoff I., Overmyer M., Helisalmi S., Soininen H. (2000). Lower counts of astroglia and activated microglia in patients with Alzheimer's disease with regular use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2, 37–46 - PubMed

