Evaluation of hydration and nutritional gels as supportive care after total-body irradiation in mice (Mus musculus)
- PMID: 20587164
- PMCID: PMC2877305
Evaluation of hydration and nutritional gels as supportive care after total-body irradiation in mice (Mus musculus)
Abstract
Concern regarding the potential for radiation exposure from accidents or nuclear and radiologic terrorism is increasing. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the addition of minimal supportive care consisting of hydration or nutritional gels could be used to reduce mortality in mice exposed to (60)Co gamma-radiation. Male CD2F1 mice received 0, 8.50, or 9.25 Gy (60)Co at a dose rate of 0.6 Gy/min. These groups were further divided into 3 treatment groups that-in addition to pelleted food and water-received no supportive care, hydration gel, or nutritional gel. Overall survival, mean survival time, consumption of pelleted food and gel, and body weight were recorded for 30 d. Radiation caused dose-dependent decreases in overall survival, consumption of pelleted food and supplemental gel, and body weight. However, at each radiation dose (0, 8.50, 9.25 Gy), the type of supportive care did not modify overall survival, mean survival time, or changes in body weight. These results demonstrate that hydration and nutritional gels were not effective methods of supportive care after high-dose total body irradiation in mice.
Figures



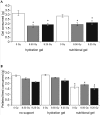
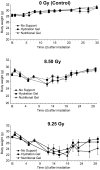
Similar articles
-
Subject-Based versus Population-Based Care after Radiation Exposure.Radiat Res. 2015 Jul;184(1):46-55. doi: 10.1667/RR13918.1. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 26121229
-
The effect of total body gamma-irradiation on mortality, egg production and egg weight of Japanese quails.Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 May;47(5):591-7. doi: 10.1080/09553008514550821. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985. PMID: 3888896
-
[Modification of radiation damage to biological objects by lasers].Aviakosm Ekolog Med. 2012 Sep-Oct;46(5):42-6. Aviakosm Ekolog Med. 2012. PMID: 23402143 Russian.
-
Effect of Pseudomonas contamination or antibiotic decontamination of the GI tract on acute radiation lethality after neutron or gamma irradiation.Radiat Res. 1985 Dec;104(3):395-405. Radiat Res. 1985. PMID: 3909210
-
A contribution to the study of damage and regeneration of hemopoiesis during fractionated irradiation and repeated bone marrow transplantation.Strahlenther Onkol. 1988 Jun;164(6):357-62. Strahlenther Onkol. 1988. PMID: 3291165 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal Care in Radiation Medical Countermeasures Studies.Radiat Res. 2022 Nov 1;198(5):514-535. doi: 10.1667/RADE-21-00211.1. Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 36001810 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Supplemental Diet Gels for Preventing Postoperative Weight Loss in Mice ( Mus musculus).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 1;62(1):87-91. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS22-000030. Epub 2022 Nov 21. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36410729 Free PMC article.
-
Study logistics that can impact medical countermeasure efficacy testing in mouse models of radiation injury.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(sup1):S151-S167. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1820599. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 32909878 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Hit Compounds Identified from High-throughput Screening for their Effect on Blood-brain Barrier Integrity and Amyloid-β Clearance: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Neuroscience. 2018 May 21;379:269-280. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29596966 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Different Commercial Dietary Supplements in the Peri-Weaning Period on Consumption and Growth Performance in C57Bl/6J Mice.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;10(8):1284. doi: 10.3390/ani10081284. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32731440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archambeau JO, Stryckmanns P, Brenneis H. 1968. The effect of food and water deprivation on the peripheral blood parameters of the mouse. Radiat Res 36:396–409 - PubMed
-
- Bing FC, Mendel LB. 1931. The relationship between food and water intake in mice. Am J sPhysiol 98:169–179
-
- Brook I, Elliott TB. 1991. Quinolone therapy in the prevention of mortality after irradiation. Radiat Res 128:100–103 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
