Identification and characterization of a novel agonistic anti-DR4 human monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 20581445
- PMCID: PMC2958577
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.2.5.12570
Identification and characterization of a novel agonistic anti-DR4 human monoclonal antibody
Abstract
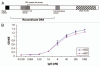
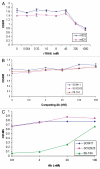
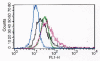
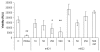
The tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its functional receptors, DR4 and DR5, have been established as promising targets for cancer treatment. Therapeutics targeting TRAIL and its receptors are not only effective in killing many types of tumors, but they also synergize with traditional therapies and show efficacy against tumors that are otherwise resistant to conventional treatments. We describe here the identification and characterization of two human monoclonal antibodies, m921 and m922, that are specific for human DR4. Both antibodies competed with TRAIL for binding to DR4, but only m921 recognized cell surface-associated DR4 and inhibited the growth of ST486 cells. This antibody may have potential for further development as a candidate therapeutic and research tool.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRAIL signaling is mediated by DR4 in pancreatic tumor cells despite the expression of functional DR5.J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Jul;88(7):729-40. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0619-0. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20354842
-
Prediction of proapoptotic anticancer therapeutic response in vivo based on cell death visualization and TRAIL death ligand-receptor interaction.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Aug 15;12(4):335-48. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.4.17174. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21785270
-
Dual Agonist Surrobody Simultaneously Activates Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 to Induce Cancer Cell Death.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Jan;15(1):114-24. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0400. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26516157 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: Are we on the right TRAIL?Cancer Treat Rev. 2009 May;35(3):280-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009. PMID: 19117685 Review.
-
Cancer: novel therapeutic strategies that exploit the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/TRAIL receptor pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(2):280-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.10.005. Epub 2006 Oct 7. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17097329 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibodies and Derivatives Targeting DR4 and DR5 for Cancer Therapy.Antibodies (Basel). 2017 Oct 25;6(4):16. doi: 10.3390/antib6040016. Antibodies (Basel). 2017. PMID: 31548531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by antibody VRC01.Science. 2010 Aug 13;329(5993):811-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1192819. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Science. 2010. PMID: 20616231 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic antibodies against cancer.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2012 Jun;26(3):447-81, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2012.02.013. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2012. PMID: 22520975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC4 degradation by combined TRAIL and valproic acid treatment induces apoptotic cell death of TRAIL-resistant head and neck cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 21;8(1):12520. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31039-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30131570 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;899:1-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-921-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22735943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashkenazi A. Directing cancer cells to self-destruct with pro-apoptotic receptor agonists. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2008;7:1001–1012. - PubMed
-
- Smith CA, Farrah T, Goodwin RG. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation and death. Cell. 1994;76:959–962. - PubMed
-
- Hymowitz SG, Christinger HW, Fuh G, Ultsch M, O'Connell M, Kelley RF, et al. Triggering cell death: the crystal structure of Apo2L/TRAIL in a complex with death receptor 5. Mole Cell. 1999;4:563–571. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann SH, Vaux DL. Alterations in the apoptotic machinery and their potential role in anticancer drug resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22:7414–7430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
