The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function
- PMID: 20576703
- PMCID: PMC2896186
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq537
The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function
Abstract
GeneMANIA (http://www.genemania.org) is a flexible, user-friendly web interface for generating hypotheses about gene function, analyzing gene lists and prioritizing genes for functional assays. Given a query list, GeneMANIA extends the list with functionally similar genes that it identifies using available genomics and proteomics data. GeneMANIA also reports weights that indicate the predictive value of each selected data set for the query. Six organisms are currently supported (Arabidopsis thaliana, Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, Mus musculus, Homo sapiens and Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and hundreds of data sets have been collected from GEO, BioGRID, Pathway Commons and I2D, as well as organism-specific functional genomics data sets. Users can select arbitrary subsets of the data sets associated with an organism to perform their analyses and can upload their own data sets to analyze. The GeneMANIA algorithm performs as well or better than other gene function prediction methods on yeast and mouse benchmarks. The high accuracy of the GeneMANIA prediction algorithm, an intuitive user interface and large database make GeneMANIA a useful tool for any biologist.
Figures
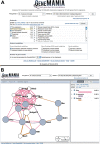
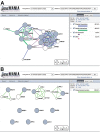
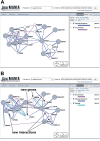
Similar articles
-
GeneMANIA prediction server 2013 update.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(Web Server issue):W115-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt533. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23794635 Free PMC article.
-
GeneMANIA update 2018.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 2;46(W1):W60-W64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky311. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29912392 Free PMC article.
-
IMP 2.0: a multi-species functional genomics portal for integration, visualization and prediction of protein functions and networks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W128-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv486. Epub 2015 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25969450 Free PMC article.
-
Combining many interaction networks to predict gene function and analyze gene lists.Proteomics. 2012 May;12(10):1687-96. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100607. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22589215 Review.
-
Biological Network Inference and analysis using SEBINI and CABIN.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:551-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381531 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value and Related Regulatory Networks of MRPL15 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 May 7;11:656172. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.656172. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34026630 Free PMC article.
-
Chapter 2: Data-driven view of disease biology.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(12):e1002816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002816. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23300408 Free PMC article.
-
Halogenated boroxine increases propensity to apoptosis in leukemia (UT-7) but not non-tumor cells in vitro.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Jan;13(1):143-153. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13522. Epub 2022 Nov 22. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 36369656 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide methylation patterns predict clinical benefit of immunotherapy in lung cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2020 Aug 6;12(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-00907-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32762727 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Bulk and Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data to Construct a Prognostic Model of Membrane Tension-Related Genes for Colon Cancer.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;10(9):1562. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10091562. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36146640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown K.R., Jurisica I. Online predicted human interaction database. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2076–2082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

