Alterations of matrix metalloproteinases in the healthy elderly with increased risk of prodromal Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20576109
- PMCID: PMC2919700
- DOI: 10.1186/alzrt44
Alterations of matrix metalloproteinases in the healthy elderly with increased risk of prodromal Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are believed to be involved in the pathologic processes behind Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we aimed to examine the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of MMPs and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in individuals with AD dementia and cognitively healthy elderly individuals, and to investigate their relationship with established CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: CSF was collected from 38 individuals with AD dementia and 34 cognitively healthy elderly individuals. The CSF was analyzed for MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, TIMP-1, beta-amyloid1-42 (Abeta42), total tau protein (T-tau) and phosphorylated tau protein (P-tau). MMP/TIMP-1 ratios were calculated. APOE genotype was determined for the participants.
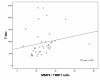
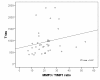
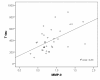
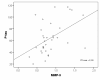
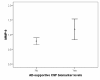
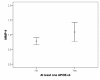
Results: AD patients had higher MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratios and lower TIMP-1 levels compared to cognitively healthy individuals. In AD patients, the MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio correlated with CSF T-tau, a marker of neurodegeneration. Interestingly, the cognitively healthy individuals with risk markers for future AD, i.e. AD-supportive CSF biomarker levels of T-tau, P-tau and Abeta42 or the presence of the APOE epsilon4 allele, had higher CSF MMP-3 and MMP-9 levels and higher CSF MMP-3/TIMP-1 ratios compared to the healthy individuals without risk markers. The CSF levels of MMP-3 and -9 in the control group also correlated with the CSF T-tau and P-tau levels.
Conclusions: This study indicates that MMP-3 and MMP-9 might be involved in early pathogenesis of AD and that MMPs could be associated with neuronal degeneration and formation of neurofibrillary tangles even prior to development of overt cognitive dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of plasma matrix metalloproteinase levels on longitudinal changes in Alzheimer's disease (AD) biomarkers and cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment due to AD registered in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative database.J Neurol Sci. 2020 Sep 15;416:116989. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116989. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32603972
-
Plasma MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio serves as a novel potential biomarker in Alzheimer's disease.Neuroreport. 2023 Oct 4;34(15):767-772. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001952. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Neuroreport. 2023. PMID: 37695608
-
Concentrations of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;40(2):351-7. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131634. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24448781
-
Current Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease: From CSF to Blood.J Pers Med. 2020 Aug 12;10(3):85. doi: 10.3390/jpm10030085. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32806668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in the pathophysiology of neurodegeneration: a literature study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;37(2):273-83. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130647. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23792694 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption in the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Missing Link between Brain and Body Inflammation in Bipolar Disorder?Neural Plast. 2015;2015:708306. doi: 10.1155/2015/708306. Epub 2015 May 13. Neural Plast. 2015. PMID: 26075104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An apolipoprotein E4 fragment affects matrix metalloproteinase 9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and cytokine levels in brain cell lines.Neuroscience. 2012 May 17;210:21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.013. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22445724 Free PMC article.
-
Functional morphology of the blood-brain barrier in health and disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Mar;135(3):311-336. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1815-1. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 29411111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Nov;121(11):1387-97. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1205-3. Epub 2014 Jul 22. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 25047909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implication of matrix metalloproteinases in regulating neuronal disorder.Mol Biol Rep. 2015 Jan;42(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3752-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25374425 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

