Vandetanib plus docetaxel versus docetaxel as second-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ZODIAC): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 20570559
- PMCID: PMC3225192
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70132-7
Vandetanib plus docetaxel versus docetaxel as second-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ZODIAC): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial
Abstract
Background: Vandetanib is a once-daily oral inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and rearranged during transfection (RET) tyrosine kinases. In a randomised phase 2 study in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), adding vandetanib 100 mg to docetaxel significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with docetaxel alone, including a longer PFS in women. These results supported investigation of the combination in this larger, definitive phase 3 trial (ZODIAC).
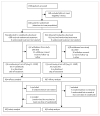
Methods: Between May, 2006, and April, 2008, patients with locally advanced or metastatic (stage IIIB-IV) NSCLC after progression following first-line chemotherapy were randomly assigned 1:1 through a third-party interactive voice system to receive vandetanib (100 mg/day) plus docetaxel (75 mg/m(2) intravenously every 21 days; maximum six cycles) or placebo plus docetaxel. The primary objective was comparison of PFS between the two groups in the intention-to-treat population. Women were a coprimary analysis population. This study has been completed and is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00312377.
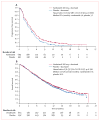
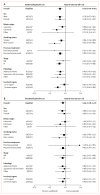
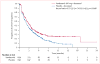
Findings: 1391 patients received vandetanib plus docetaxel (n=694 [197 women]) or placebo plus docetaxel (n=697 [224 women]). Vandetanib plus docetaxel led to a significant improvement in PFS versus placebo plus docetaxel (hazard ratio [HR] 0.79, 97.58% CI 0.70-0.90; p<0.0001); median PFS was 4.0 months in the vandetanib group versus 3.2 months in placebo group. A similar improvement in PFS with vandetanib plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel was seen in women (HR 0.79, 0.62-1.00, p=0.024); median PFS was 4.6 months in the vandetanib group versus 4.2 months in the placebo group. Among grade 3 or higher adverse events, rash (63/689 [9%] vs 7/690 [1%]), neutropenia (199/689 [29%] vs 164/690 [24%]), leukopenia (99/689 [14%] vs 77/690 [11%]), and febrile neutropenia (61/689 [9%] vs 48/690 [7%]) were more common with vandetanib plus docetaxel than with placebo plus docetaxel. The most common serious adverse event was febrile neutropenia (46/689 [7%] in the vandetanib group vs 38/690 [6%] in the placebo group).
Interpretation: The addition of vandetanib to docetaxel provides a significant improvement in PFS in patients with advanced NSCLC after progression following first-line therapy.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
RSH received fees for consultancy (AstraZeneca steering committee) and grant support from AstraZeneca. WEEE received fees for an advisory board (ZODIAC steering committee) and a speaker’s bureau from AstraZeneca. PG received fees for an advisory board (ZODIAC steering committee) and accommodation expenses from AstraZeneca. YI received fees for honoraria from AstraZeneca. LZ received fees from AstraZeneca for presentation of data from this study at a regional meeting. JVH received fees for consultancy, grants, and honoraria from AstraZeneca. PL, SJK, and HT are employees of AstraZeneca and PL has stock in the company. BEJ received grant support, consultancy and honoraria fees (ZODIAC steering committee), and travel support from AstraZeneca. All other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
One more fallen star--ZODIAC and its implications.Lancet Oncol. 2010 Jul;11(7):604-5. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70149-2. Lancet Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20610317 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): a phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Feb;15(2):143-55. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70586-2. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24411639 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, placebo-controlled phase II study of vandetanib plus docetaxel in previously treated non small-cell lung cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2007 Sep 20;25(27):4270-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.5122. J Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17878479 Clinical Trial.
-
Double-blind, randomized trial of docetaxel plus vandetanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in platinum-pretreated metastatic urothelial cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Feb 10;30(5):507-12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.7002. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22184381 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vandetanib (ZD6474), a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinases: current status and future directions.Oncologist. 2009 Apr;14(4):378-90. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0261. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Oncologist. 2009. PMID: 19349511 Review.
-
Vandetanib: An overview of its clinical development in NSCLC and other tumors.Drugs Today (Barc). 2010 Sep;46(9):683-98. doi: 10.1358/dot.2010.46.9.1516989. Drugs Today (Barc). 2010. PMID: 20967300 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics, dynamics and toxicity of docetaxel: Why the Japanese dose differs from the Western dose.Cancer Sci. 2015 May;106(5):497-504. doi: 10.1111/cas.12647. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25728850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenic treatments in advanced NSCLC: back to the drawing board.J Thorac Dis. 2012 Dec;4(6):643-6. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.10.11. J Thorac Dis. 2012. PMID: 23205293 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nintedanib in NSCLC: evidence to date and place in therapy.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2016 May;8(3):188-97. doi: 10.1177/1758834016630976. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27239237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiangiogenic agents in the management of non-small cell lung cancer: where do we stand now and where are we headed?Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Mar;13(5):247-63. doi: 10.4161/cbt.19594. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22481432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overall response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival with targeted and standard therapies in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: US Food and Drug Administration trial-level and patient-level analyses.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar 20;33(9):1008-14. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.0489. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25667291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Cancer factsheet. 2009 http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/ (accessed)
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, et al. Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2095–103. - PubMed
-
- Fossella FV, DeVore R, Kerr RN, et al. Randomized phase III trial of docetaxel versus vinorelbine or ifosfamide in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy regimens. The TAX 320 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2354–62. - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

