Initiation of antiretroviral therapy at higher nadir CD4+ T-cell counts is associated with reduced arterial stiffness in HIV-infected individuals
- PMID: 20543654
- PMCID: PMC2903431
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833bee44
Initiation of antiretroviral therapy at higher nadir CD4+ T-cell counts is associated with reduced arterial stiffness in HIV-infected individuals
Abstract
Objective: HIV infection is associated with increased rates of cardiovascular disease. We sought to evaluate whether initiation of HIV therapy at higher nadir CD4(+) T-cell counts might reduce cardiovascular risk, as measured by arterial stiffness.
Design: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 80 HIV-infected men who were antiretroviral-treated with undetectable plasma HIV RNA levels.
Methods: Participants underwent noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness by pulse wave analysis (augmentation index normalized for heart rate of 75 bpm) and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, both sensitive measures of cardiovascular risk. A generalized linear model was used to determine the relationship between cardiovascular and HIV-related predictors, and arterial stiffness.
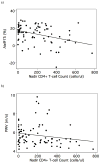
Results: In unadjusted analyses, predictors of arterial stiffness included age, blood pressure, antihypertensive medication use, and nadir CD4(+) T-cell count below 350 cells/microl (all P < 0.05). After adjusting for both cardiovascular risk factors (age, blood pressure, antihypertensive medication use, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking) and HIV-related covariates, nadir CD4(+) T-cell count below 350 cells/microl was independently associated with a 0.41 m/s increase in pulse wave velocity (95% confidence interval 0.03-0.79, P = 0.03) and a 7.3% increase in augmentation index (augmentation index normalized for heart rate of 75 bpm; 95% confidence interval 2.6-11.9, P = 0.003). Neither duration of antiretroviral therapy nor exposure to protease inhibitors was associated with arterial stiffness.
Conclusion: Among treated HIV-infected individuals, arterial stiffness is independently associated with both traditional cardiovascular risk factors as well as a low nadir CD4(+) T-cell count. Our data suggest that cardiovascular risk among HIV-infected individuals could be reduced through early initiation of antiretroviral therapy, before CD4 T-cell counts are depressed, a concept that should be tested prospectively in future studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association of CD4+ T-cell counts and cardiovascular risk in treated HIV disease.AIDS. 2012 Jun 1;26(9):1115-20. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328352ce54. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22382147 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic stiffness aging is influenced by past profound immunodeficiency in HIV-infected individuals: results from the EVAS-HIV (EValuation of Aortic Stiffness in HIV-infected individuals).J Hypertens. 2016 Jul;34(7):1338-46. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000957. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27137177
-
Is arterial stiffness in HIV-infected individuals associated with HIV-related factors?Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 Sep;45(9):818-26. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2012007500116. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012. PMID: 22782555 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal time for initiation of antiretroviral therapy in asymptomatic, HIV-infected, treatment-naive adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;2010(3):CD008272. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008272.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20238364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initiation of antiretroviral therapy at high CD4 cell counts: does it reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease?Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014 Jan;9(1):54-62. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000015. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014. PMID: 24275676 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving mechanisms and presentations of cardiovascular disease in people with HIV: implications for management.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Mar 14;37(1):e0009822. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00098-22. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38299802 Review.
-
Elevated Markers of Vascular Remodeling and Arterial Stiffness Are Associated With Neurocognitive Function in Older HIV+ Adults on Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017 Feb 1;74(2):134-141. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001230. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017. PMID: 27828873 Free PMC article.
-
HIV infection and arterial stiffness among older-adults taking antiretroviral therapy in rural Uganda.AIDS. 2016 Feb 20;30(4):667-70. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000992. AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26636926 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune evasion strategies by human immunodeficiency virus type 1.ISRN AIDS. 2013 Aug 12;2013:954806. doi: 10.1155/2013/954806. ISRN AIDS. 2013. PMID: 24052891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise to Prevent Accelerated Vascular Aging in People Living With HIV.Circ Res. 2024 May 24;134(11):1607-1635. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.323975. Epub 2024 May 23. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38781293 Review.
References
-
- Friis-Møller N, Sabin CA, Weber R, d’Arminio Monforte A, El-Sadr WM, Reiss P, et al. Combination antiretroviral therapy and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1993–2003. - PubMed
-
- Holmberg SD, Moorman AC, Williamson JM, Tong TC, Ward DJ, Wood KC, et al. Protease inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with HIV-1. Lancet. 2002;360:1747–1748. - PubMed
-
- Hsue PY, Hunt PW, Sinclair E, Bredt B, Franklin A, Killian M, et al. Increased carotid intima-media thickness in HIV patients is associated with increased cytomegalovirus-specific T-cell responses. AIDS. 2006;20:2275–2283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K23 AI066885/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-MH59037/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763-129011/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095130-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5K23-AI066885/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01-HL095130/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24-AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH059037-13/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095130/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI27763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763-12/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI066885-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI069994-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials