Effect of high-dose allopurinol on exercise in patients with chronic stable angina: a randomised, placebo controlled crossover trial
- PMID: 20542554
- PMCID: PMC2890860
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60391-1
Effect of high-dose allopurinol on exercise in patients with chronic stable angina: a randomised, placebo controlled crossover trial
Abstract
Background: Experimental evidence suggests that xanthine oxidase inhibitors can reduce myocardial oxygen consumption for a particular stroke volume. If such an effect also occurs in man, this class of inhibitors could become a new treatment for ischaemia in patients with angina pectoris. We ascertained whether high-dose allopurinol prolongs exercise capability in patients with chronic stable angina.
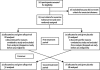
Methods: 65 patients (aged 18-85 years) with angiographically documented coronary artery disease, a positive exercise tolerance test, and stable chronic angina pectoris (for at least 2 months) were recruited into a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover study in a hospital and two infirmaries in the UK. We used computer-generated randomisation to assign patients to allopurinol (600 mg per day) or placebo for 6 weeks before crossover. Our primary endpoint was the time to ST depression, and the secondary endpoints were total exercise time and time to chest pain. We did a completed case analysis. This study is registered as an International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial, number ISRCTN 82040078.
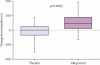
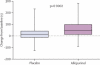
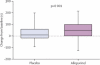
Findings: In the first treatment period, 31 patients were allocated to allopurinol and 28 were analysed, and 34 were allocated to placebo and 32 were analysed. In the second period, all 60 patients were analysed. Allopurinol increased the median time to ST depression to 298 s (IQR 211-408) from a baseline of 232 s (182-380), and placebo increased it to 249 s (200-375; p=0.0002). The point estimate (absolute difference between allopurinol and placebo) was 43 s (95% CI 31-58). Allopurinol increased median total exercise time to 393 s (IQR 280-519) from a baseline of 301 s (251-447), and placebo increased it to 307 s (232-430; p=0.0003); the point estimate was 58 s (95% CI 45-77). Allopurinol increased the time to chest pain from a baseline of 234 s (IQR 189-382) to 304 s (222-421), and placebo increased it to 272 s (200-380; p=0.001); the point estimate was 38 s (95% CI 17-55). No adverse effects of treatment were reported.
Interpretation: Allopurinol seems to be a useful, inexpensive, well tolerated, and safe anti-ischaemic drug for patients with angina.
Funding: British Heart Foundation.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Allopurinol for chronic stable angina: old drug, new tricks?Lancet. 2010 Jun 19;375(9732):2126-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60578-8. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20542555 No abstract available.
-
Is allopurinol a potential new treatment for angina pectoris?Future Cardiol. 2010 Sep;6(5):575-7. doi: 10.2217/fca.10.88. Future Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20932107 No abstract available.
-
High-dose allopurinol in patients with stable angina pectoris.Lancet. 2010 Oct 16;376(9749):1298; author reply 1299-300. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61910-1. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20951883 No abstract available.
-
High-dose allopurinol in patients with stable angina pectoris.Lancet. 2010 Oct 16;376(9749):1298-9; author reply 1299-300. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61911-3. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20951884 No abstract available.
-
High-dose allopurinol in patients with stable angina pectoris.Lancet. 2010 Oct 16;376(9749):1299; author reply 1299-300. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61912-5. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20951887 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic insights into the therapeutic use of high-dose allopurinol in angina pectoris.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Aug 16;58(8):820-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.052. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21835317 Clinical Trial.
-
Additional antianginal and anti-ischemic efficacy of mibefradil in patients concomitantly treated with long-acting nitrates for chronic stable angina pectoris.Clin Cardiol. 1998 Jul;21(7):483-90. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960210707. Clin Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9669057 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of bepridil on exercise tolerance in chronic stable angina: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial.Am J Cardiol. 1984 Mar 1;53(6):679-83. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90385-0. Am J Cardiol. 1984. PMID: 6367414 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of intermittent (eight hours off) transdermal nitrate therapy in stable angina.Int J Cardiol. 1994 Mar 1;43(3):251-6. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(94)90205-4. Int J Cardiol. 1994. PMID: 8181883 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of trimetazidine in stable angina: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, controlled trials.Coron Artery Dis. 2003 Apr;14(2):171-9. doi: 10.1097/00019501-200304000-00010. Coron Artery Dis. 2003. PMID: 12655281 Review.
Cited by
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors treatment or discontinuation effects on mortality: evidence of xanthine oxidase inhibitors withdrawal syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1289386. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1289386. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38259292 Free PMC article.
-
Urate-lowering therapy may mitigate the risks of hospitalized stroke and mortality in patients with gout.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 23;15(6):e0234909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234909. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32574194 Free PMC article.
-
[Hyperuricemia - more than gout : Impact on cardiovascular risk and renal insufficiency].Z Rheumatol. 2015 May;74(4):322-8. doi: 10.1007/s00393-014-1481-1. Z Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25962453 Review. German.
-
Hyperuricemia in Kidney Disease: A Major Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Events, Vascular Calcification, and Renal Damage.Semin Nephrol. 2020 Nov;40(6):574-585. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.12.004. Semin Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33678312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Serum Uric Acid Level on Systemic Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with a Broad Spectrum of Ischemic Heart Disease.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 30;10(19):4530. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194530. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34640550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ekelund UE, Harrison RW, Shokek O. Intravenous allopurinol decreases myocardial oxygen consumption and increases mechanical efficiency in dogs with pacing-induced heart failure. Circ Res. 1999;85:437–445. - PubMed
-
- Ukai T, Cheng CP, Tachibana H. Allopurinol enhances the contractile response to dobutamine and exercise in dogs with pacing-induced heart failure. Circulation. 2001;103:750–755. - PubMed
-
- Cappola TP, Kass DA, Nelson GS. Allopurinol improves myocardial efficiency in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2001;104:2407–2411. - PubMed
-
- Perez NG, Gao WD, Marban E. Novel myofilament Ca2+-sensitizing property of xanthine oxidase inhibitors. Circ Res. 1998;83:423–430. - PubMed
-
- Stull LB, Leppo MK, Szweda L, Gao WD, Marban E. Chronic treatment with allopurinol boosts survival and cardiac contractility in murine postischemic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2004;95:1005–1011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical