The laforin-malin complex, involved in Lafora disease, promotes the incorporation of K63-linked ubiquitin chains into AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunits
- PMID: 20534808
- PMCID: PMC2912345
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e10-03-0227
The laforin-malin complex, involved in Lafora disease, promotes the incorporation of K63-linked ubiquitin chains into AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunits
Abstract
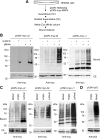
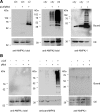
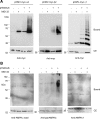
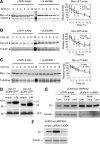
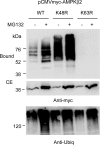
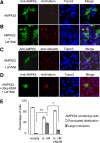
Lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder caused by defects in the function of at least two proteins: laforin, a dual-specificity protein phosphatase, and malin, an E3-ubiquitin ligase. In this study, we report that a functional laforin-malin complex promotes the ubiquitination of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a serine/threonine protein kinase that acts as a sensor of cellular energy status. This reaction occurs when any of the three AMPK subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma) are expressed individually in the cell, and it also occurs on AMPK beta when it is part of a heterotrimeric complex. We also report that the laforin-malin complex promotes the formation of K63-linked ubiquitin chains, which are not involved in proteasome degradation. On the contrary, this modification increases the steady-state levels of at least AMPK beta subunit, possibly because it leads to the accumulation of this protein into inclusion bodies. These results suggest that the modification introduced by the laforin-malin complex could affect the subcellular distribution of AMPK beta subunits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lafora disease proteins malin and laforin are recruited to aggresomes in response to proteasomal impairment.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Apr 1;16(7):753-62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm006. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17337485
-
Laforin, a dual-specificity phosphatase involved in Lafora disease, is phosphorylated at Ser25 by AMP-activated protein kinase.Biochem J. 2011 Oct 15;439(2):265-75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110150. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21728993 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of glycogen synthesis by the laforin-malin complex is modulated by the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway.Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Mar 1;17(5):667-78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm339. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Hum Mol Genet. 2008. PMID: 18029386
-
Deciphering the role of malin in the lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy.IUBMB Life. 2012 Oct;64(10):801-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.1072. Epub 2012 Jul 20. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22815132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lafora disease: Current biology and therapeutic approaches.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022 Apr;178(4):315-325. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022. PMID: 34301405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Laforin, a protein with many faces: glucan phosphatase, adapter protein, et alii.FEBS J. 2013 Jan;280(2):525-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08549.x. Epub 2012 Mar 16. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 22364389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycogen and its metabolism: some new developments and old themes.Biochem J. 2012 Feb 1;441(3):763-87. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111416. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22248338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Translational Readthrough on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Targeted by Premature Termination Codon Mutations in Human Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2743:1-19. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3569-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38147205
-
1q21.1 Duplication syndrome and epilepsy: Case report and review.Neurol Genet. 2018 Jan 18;4(1):e219. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000219. eCollection 2018 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29379884 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Laforin is required for the functional activation of malin in endoplasmic reticulum stress resistance in neuronal cells.FEBS J. 2012 Jul;279(14):2467-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08627.x. Epub 2012 Jun 8. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22578008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bateman A. The structure of a domain common to archaebacteria and the homocystinuria disease protein. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997;22:12–13. - PubMed
-
- Crute B. E., Seefeld K., Gamble J., Kemp B. E., Witters L. A. Functional domains of the alpha1 catalytic subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:35347–35354. - PubMed
-
- Chan E. M., Omer S., Ahmed M., Bridges L. R., Bennett C., Scherer S. W., Minassian B. A. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy with polyglucosans (Lafora disease): evidence for a third locus. Neurology. 2004;63:565–567. - PubMed
-
- Chan E. M., et al. Mutations in NHLRC1 cause progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 2003;35:125–127. - PubMed

