Amphiregulin promotes intestinal epithelial regeneration: roles of intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts
- PMID: 20534719
- PMCID: PMC2940516
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-0319
Amphiregulin promotes intestinal epithelial regeneration: roles of intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts
Abstract
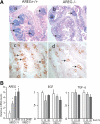
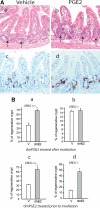
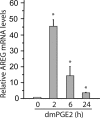
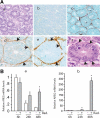
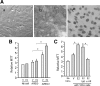
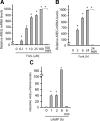
Epidermal growth factor family plays critical roles in intestinal epithelial proliferation and differentiation. The precise function of amphiregulin (AREG), a member of the epidermal growth factor family, in intestinal biology is largely unknown. The present study attempted to address the functional roles of AREG in intestinal epithelial regeneration. Total body irradiation was performed, and intestinal regeneration was assessed in AREG knockout mice. Genetically disruption of AREG significantly impaired intestinal regeneration after radiation injury. It is known that prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) exerts radio-protective and growth-stimulatory effects on intestinal epithelium. We found that PGE(2) radio-protective action did not involve AREG. However, PGE(2) growth-stimulatory effects required functional AREG. Localization of AREG expression was determined by immunohistochemistry in regenerative intestine. The immunoreactivity of AREG was predominantly localized in intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts (ISEMF). Primary ISEMF cultures were established, and growth-stimulatory actions of ISEMF-generated AREG were demonstrated in cell coculture system. In addition, we found that the cAMP/protein kinase A pathway robustly induced AREG in cultured ISEMF. These studies suggest that AREG plays critical roles in intestinal epithelial growth. Modulation of levels of AREG by targeting ISEMF represents a novel strategy for treatment of certain intestinal disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pro-neoplastic effects of amphiregulin in colorectal carcinogenesis.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2013 Jun;44(2):211-21. doi: 10.1007/s12029-012-9474-2. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23263765
-
Amphiregulin-dependent mucous cell metaplasia in a model of nonallergic lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;47(3):349-57. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0257OC. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22493011 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine and autocrine regulation of epidermal growth factor-like factors in cumulus oocyte complexes and granulosa cells: key roles for prostaglandin synthase 2 and progesterone receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Jun;20(6):1352-65. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0504. Epub 2006 Mar 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16543407
-
The multiple roles of amphiregulin in human cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1816(2):119-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21658434 Review.
-
Amphiregulin in infectious diseases: Role, mechanism, and potential therapeutic targets.Microb Pathog. 2024 Jan;186:106463. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106463. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38036111 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of resistant starch in improving gut health, adiposity, and insulin resistance.Adv Nutr. 2015 Mar 13;6(2):198-205. doi: 10.3945/an.114.007419. Print 2015 Mar. Adv Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25770258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and nuclear β-catenin induced by conditional intestinal disruption of Cdh1 with Apc is E-cadherin EC1 domain dependent.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 25;7(43):69883-69902. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11513. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27566565 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue regulatory T cells.Immunology. 2020 Sep;161(1):4-17. doi: 10.1111/imm.13208. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32463116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the impact of antibiotic-induced dysbiosis on protection from Clostridium difficile colitis by mouse colonic innate lymphoid cells.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0333823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03338-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38376154 Free PMC article.
-
The human adenocarcinoma-associated gene, AGR2, induces expression of amphiregulin through Hippo pathway co-activator YAP1 activation.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 20;286(20):18301-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.215707. Epub 2011 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babyatsky MW, Podolsky DK 1991 Growth and development in the gastrointestinal tract. In: Yamada T, Alpers DH, Owyang C, Powell DW, Silverstein FE, eds. Textbook of gastroenterology. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Co.; 475–501
-
- Lowry SF 1990 The route of feeding influences injury responses. J Trauma 30:S10–S15 - PubMed
-
- Steinmetz OK, Meakins JL 1991 Care of the gut in the surgical intensive care unit. Fact or fashion? Can J Surg 34:207–215 - PubMed
-
- Ray EC, Avissar NE, Sax HC 2002 Growth factor regulation of enterocyte nutrient transport during intestinal adaptation. A J Surg 183:361–371 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

