Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis
- PMID: 20530205
- PMCID: PMC2901067
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092474
Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis
Abstract
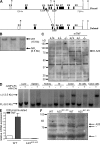
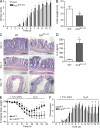
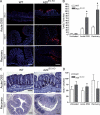
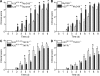
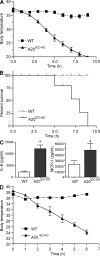
A20 is a nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) target gene that encodes a ubiquitin-editing enzyme that is essential for the termination of NF-kappaB activation after tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or microbial product stimulation and for the prevention of TNF-induced apoptosis. Mice lacking A20 succumb to inflammation in several organs, including the intestine, and A20 mutations have been associated with Crohn's disease. However, ablation of NF-kappaB activity, specifically in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), promotes intestinal inflammation. As A20 deficiency sensitizes cells to TNF-induced apoptosis yet also promotes NF-kappaB activity, it is not clear if A20 deficiency in IECs would exacerbate or ameliorate intestinal inflammation. We generated mice lacking A20 specifically in IECs. These mice did not show spontaneous intestinal inflammation but exhibited increased susceptibility to experimental colitis, and their IECs were hypersensitive to TNF-induced apoptosis. The resulting TNF-driven breakdown of the intestinal barrier permitted commensal bacterial infiltration and led to systemic inflammation. These studies define A20 as a major antiapoptotic protein in the intestinal epithelium and further indicate that defects in A20 might contribute to inflammatory bowel disease in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FADD prevents RIP3-mediated epithelial cell necrosis and chronic intestinal inflammation.Nature. 2011 Jul 31;477(7364):330-4. doi: 10.1038/nature10273. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21804564
-
A20 controls intestinal homeostasis through cell-specific activities.Nat Commun. 2014 Sep 30;5:5103. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6103. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25267258
-
Expression of TNFAIP3 in intestinal epithelial cells protects from DSS- but not TNBS-induced colitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Jul 15;303(2):G220-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00077.2012. Epub 2012 May 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22595989 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of immunopathology.Trends Immunol. 2009 Aug;30(8):383-91. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Trends Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19643665 Review.
-
A20 in inflammation and autoimmunity.Trends Immunol. 2014 Jan;35(1):22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Trends Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24246475 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of NF-κB-dependent gene transcription using programmable DNA minor groove binders.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 24;109(4):1023-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118506109. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22203967 Free PMC article.
-
Host-microbiota interactions in inflammatory bowel disease.Gut Microbes. 2012 Jul-Aug;3(4):332-44. doi: 10.4161/gmic.20228. Epub 2012 May 10. Gut Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22572873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repressive Control of Keratinocyte Cytoplasmic Inflammatory Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):11943. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511943. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herbs-partitioned moxibustion alleviates aberrant intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis by upregulating A20 expression in a mouse model of Crohn's disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 May 7;25(17):2071-2085. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2071. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31114134 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of NF-κB and its involvement in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 31;13(3):221. doi: 10.1186/ar3324. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21639951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

