mTOR signaling in cancer cell motility and tumor metastasis
- PMID: 20528734
- PMCID: PMC2883790
- DOI: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v20.i1.10
mTOR signaling in cancer cell motility and tumor metastasis
Abstract
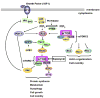
Tumor cell migration is a key step in the formation of cancer metastasis. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed serinethreonine kinase, has been intensely studied for over a decade as a central regulator of cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Recent data have shown that mTOR also plays a critical role in the regulation of tumor cell motility and cancer metastasis. Here, we briefly review recent advances regarding mTOR signaling in tumor cell motility. We also discuss recent findings about the mechanism by which rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of mTOR, inhibits cell motility in vitro and metastasis in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of mTOR signaling in tumor cell motility, invasion and metastasis.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011 Feb;12(1):30-42. doi: 10.2174/138920311795659407. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011. PMID: 21190521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin inhibits IGF-1 stimulated cell motility through PP2A pathway.PLoS One. 2010 May 11;5(5):e10578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010578. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20485667 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent liver cyst growth in polycystin-2-defective mice.Hepatology. 2010 May;51(5):1778-88. doi: 10.1002/hep.23511. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20131403 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 insulin-like growth factor regulates MT1-MMP synthesis and tumor invasion via PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling.Oncogene. 2003 Feb 20;22(7):974-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206197. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12592384
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): conducting the cellular signaling symphony.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14071-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.094003. Epub 2010 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20231296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Skeletal metastasis: treatments, mouse models, and the Wnt signaling.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Jul;32(7):380-96. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10218. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23327798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA in glioma: signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):27582-27592. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15175. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28187439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA-21 governs TORC1 activation in renal cancer cell proliferation and invasion.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037366. Epub 2012 Jun 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22685542 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Quercetin via the Akt/AMPK/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling Cascade.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 10;11(6):e0157251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157251. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27285995 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C results in loss of mesenchymal traits in metastatic breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 19;14(2):R50. doi: 10.1186/bcr3151. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22429397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abizaid A, Lansky AJ, Fitzgerald PJ, Tanajura LF, Feres F, Staico R, Mattos L, Abizaid A, Chaves A, Centemero M, Sousa AG, Sousa JE, Zaugg MJ, Schwartz LB. Percutaneous coronary revascularization using a trilayer metal phosphorylcholine-coated zotarolimus-eluting stent. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99:1403–1408. - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT. Mammalian target of rapamycin: immunosuppressive drugs uncover a novel pathway of cytokine receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Kozlowski MT, Weng QP, Morrice N, Avruch J. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) phosphorylates and activates the p70 S6 kinase in vivo and in vitro. Curr Biol. 1998;8:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Alper O, Bergmann-Leitner ES, Bennett TA, Hacker NF, Stromberg K, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and the invasive phenotype of ovarian carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1375–1384. - PubMed
-
- Attoub S, Noe V, Pirola L, Bruyneel E, Chastre E, Mareel M, Wymann MP, Gespach C. Leptin promotes invasiveness of kidney and colonic epithelial cells via phosphoinositide 3-kinase-, rho-, and rac-dependent signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2000;14:2329–2938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

