Identification of a novel putative pancreatic stem/progenitor cell marker DCAMKL-1 in normal mouse pancreas
- PMID: 20522640
- PMCID: PMC2928534
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00146.2010
Identification of a novel putative pancreatic stem/progenitor cell marker DCAMKL-1 in normal mouse pancreas
Abstract
Stem cells are critical in maintaining adult homeostasis and have been proposed to be the origin of many solid tumors, including pancreatic cancer. Here we demonstrate the expression patterns of the putative intestinal stem cell marker DCAMKL-1 in the pancreas of uninjured C57BL/6 mice compared with other pancreatic stem/progenitor cell markers. We then determined the viability of isolated pancreatic stem/progenitor cells in isotransplantation assays following DCAMKL-1 antibody-based cell sorting. Sorted cells were grown in suspension culture and injected into the flanks of athymic nude mice. Here we report that DCAMKL-1 is expressed in the main pancreatic duct epithelia and islets, but not within acinar cells. Coexpression was observed with somatostatin, NGN3, and nestin, but not glucagon or insulin. Isolated DCAMKL-1+ cells formed spheroids in suspension culture and induced nodule formation in isotransplantation assays. Analysis of nodules demonstrated markers of early pancreatic development (PDX-1), glandular epithelium (cytokeratin-14 and Ep-CAM), and isletlike structures (somatostatin and secretin). These data taken together suggest that DCAMKL-1 is a novel putative stem/progenitor marker, can be used to isolate normal pancreatic stem/progenitors, and potentially regenerates pancreatic tissues. This may represent a novel tool for regenerative medicine and a target for anti-stem cell-based therapeutics in pancreatic cancer.
Figures
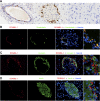
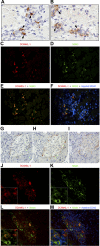
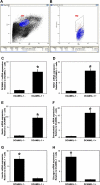

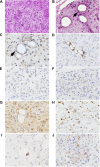
Comment in
-
DCAMKL-1: a new horizon for pancreatic progenitor identification.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Aug;299(2):G301-2. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00259.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20539004 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1 and leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor mark quiescent and cycling intestinal stem cells, respectively.Stem Cells. 2009 Oct;27(10):2571-9. doi: 10.1002/stem.193. Stem Cells. 2009. PMID: 19676123 Free PMC article.
-
Multipotential nestin-positive stem cells isolated from adult pancreatic islets differentiate ex vivo into pancreatic endocrine, exocrine, and hepatic phenotypes.Diabetes. 2001 Mar;50(3):521-33. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.3.521. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11246871
-
Activation of nestin-positive duct stem (NPDS) cells in pancreas upon neogenic motivation and possible cytodifferentiation into insulin-secreting cells from NPDS cells.Dev Dyn. 2004 May;230(1):1-11. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20012. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15108304
-
Direct lineage tracing reveals the ontogeny of pancreatic cell fates during mouse embryogenesis.Mech Dev. 2003 Jan;120(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00330-1. Mech Dev. 2003. PMID: 12490294 Review.
-
Nestin expression--a property of multi-lineage progenitor cells?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Oct;61(19-20):2510-22. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4144-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15526158 Review.
Cited by
-
Islet-derived stem cells from adult rats participate in the repair of islet damage.J Mol Histol. 2012 Dec;43(6):745-50. doi: 10.1007/s10735-012-9447-6. Epub 2012 Sep 13. J Mol Histol. 2012. PMID: 22972433
-
Deletion of Histone Methyltransferase G9a Suppresses Mutant Kras-driven Pancreatic Carcinogenesis.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020 Nov-Dec;17(6):695-705. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20224. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 33099471 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of miRNAs by agents targeting the tumor stem cell markers DCLK1, MSI1, LGR5, and BMI1.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Aug 1;1(4):217-222. doi: 10.1007/s40495-014-0006-6. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26366338 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into pancreatic cancer stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Apr 26;7(3):547-55. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i3.547. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25914762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based delivery of siDCAMKL-1 increases microRNA-144 and inhibits colorectal cancer tumor growth via a Notch-1 dependent mechanism.J Nanobiotechnology. 2011 Sep 19;9:40. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-40. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011. PMID: 21929751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agudo J, Ayuso E, Jimenez V, Salavert A, Casellas A, Tafuro S, Haurigot V, Ruberte J, Segovia JC, Bueren J, Bosch F. IGF-I mediates regeneration of endocrine pancreas by increasing beta cell replication through cell cycle protein modulation in mice. Diabetologia 51: 1862–1872, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Cirulli V, Crisa L, Beattie GM, Mally MI, Lopez AD, Fannon A, Ptasznik A, Inverardi L, Ricordi C, Deerinck T, Ellisman M, Reisfeld RA, Hayek A. KSA antigen Ep-CAM mediates cell-cell adhesion of pancreatic epithelial cells: morphoregulatory roles in pancreatic islet development. J Cell Biol 140: 1519–1534, 1998 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Donadoni C, Salani S, Del Bo R, Strazzer S, Bresolin N, Comi GP. Identification of a primitive brain-derived neural stem cell population based on aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Stem Cells 24: 975–985, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

