Synaptic correlates of increased cognitive vulnerability with aging: peripheral immune challenge and aging interact to disrupt theta-burst late-phase long-term potentiation in hippocampal area CA1
- PMID: 20519534
- PMCID: PMC2891807
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5172-09.2010
Synaptic correlates of increased cognitive vulnerability with aging: peripheral immune challenge and aging interact to disrupt theta-burst late-phase long-term potentiation in hippocampal area CA1
Abstract
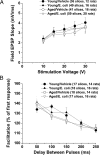
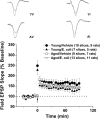
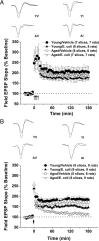
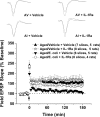
Variability in cognitive functioning increases markedly with age, as does cognitive vulnerability to physiological and psychological challenges. Exploring the basis of this vulnerability may provide important insights into the mechanisms underlying aging-associated cognitive decline. As we have previously reported, the cognitive abilities of aging (24-month-old) F344 x BN rats are generally good, but are more vulnerable to the consequences of a peripheral immune challenge (an intraperitoneal injection of live Escherichia coli) than those of their younger (3-month-old) counterparts. Four days after the injection, the aging, but not the young rats show profound memory deficits, specific to the consolidation of hippocampus-dependent memory processes. Here, we have extended these observations, using hippocampal slices to examine for the first time the combined effects of aging and a recent infection on several forms of synaptic plasticity. We have found that the specific deficit in long-lasting memory observed in the aged animals after infection is mirrored by a specific deficit in a form of long-lasting synaptic plasticity. The late-phase long-term potentiation induced in area CA1 using theta-burst stimulation is particularly compromised by the combined effects of aging and infection-a deficit that can be ameliorated by intra-cisterna magna administration of the naturally occurring antiinflammatory cytokine IL-1Ra (interleukin-1 receptor antagonist). These data support the idea that the combination of aging and a negative life event such as an infection might produce selective, early-stage failures of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus, with corresponding selective deficits in memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aging and a peripheral immune challenge interact to reduce mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor and activation of TrkB, PLCgamma1, and ERK in hippocampal synaptoneurosomes.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 16;31(11):4274-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5818-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21411668 Free PMC article.
-
Theta-frequency synaptic potentiation in CA1 in vitro distinguishes cognitively impaired from unimpaired aged Fischer 344 rats.J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 15;22(22):9932-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-22-09932.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12427850 Free PMC article.
-
Chelation of hippocampal zinc enhances long-term potentiation and synaptic tagging/capture in CA1 pyramidal neurons of aged rats: implications to aging and memory.Aging Cell. 2017 Feb;16(1):136-148. doi: 10.1111/acel.12537. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Aging Cell. 2017. PMID: 27633878 Free PMC article.
-
Aging, synaptic dysfunction, and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012 Jun;67(6):611-25. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls118. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22503992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Perfect Cytokine Storm: How Peripheral Immune Challenges Impact Brain Plasticity & Memory Function in Aging.Brain Plast. 2021 Aug 23;7(1):47-60. doi: 10.3233/BPL-210127. eCollection 2021. Brain Plast. 2021. PMID: 34631420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-1β Modulates Synaptic Transmission and Synaptic Plasticity During the Acute Phase of Sepsis in the Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Hippocampus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;13:637703. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.637703. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33643027 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β suppresses cLTP-induced surface expression of GluA1 and actin polymerization via ceramide-mediated Src activation.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Apr 30;15(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1158-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29712570 Free PMC article.
-
Do stress markers and anesthetic technique predict delirium in the elderly?Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014;38(5-6):366-74. doi: 10.1159/000363762. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014. PMID: 25171689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Synapse-specific IL-1 receptor subunit reconfiguration augments vulnerability to IL-1β in the aged hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 8;112(36):E5078-87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1514486112. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26305968 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium dysregulation and neuroinflammation: discrete and integrated mechanisms for age-related synaptic dysfunction.Ageing Res Rev. 2013 Sep;12(4):982-95. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Ageing Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 23751484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bach ME, Barad M, Son H, Zhuo M, Lu YF, Shih R, Mansuy I, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER. Age-related defects in spatial memory are correlated with defects in the late phase of hippocampal long-term potentiation in vitro and are attenuated by drugs that enhance the cAMP signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:5280–5285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes CA, McNaughton BL. An age comparison of the rates of acquisition and forgetting of spatial information in relation to long-term enhancement of hippocampal synapses. Behav Neurosci. 1985;99:1040–1048. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Memory for context is impaired by a post context exposure injection of interleukin-1beta into dorsal hippocampus. Behav Brain Res. 2002;134:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Biedenkapp JC, Sprunger DB, Wright-Hardesty KJ, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Peripheral infection and aging interact to impair hippocampal memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:723–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
