Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL#3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 20517305
- PMCID: PMC3180711
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.218
Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL#3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Objectives: VSL#3 is a high-potency probiotic mixture that has been used successfully in the treatment of pouchitis. The primary end point of the study was to assess the effects of supplementation with VSL#3 in patients affected by relapsing ulcerative colitis (UC) who are already under treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid (ASA) and/or immunosuppressants at stable doses.
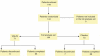
Methods: A total of 144 consecutive patients were randomly treated for 8 weeks with VSL#3 at a dose of 3,600 billion CFU/day (71 patients) or with placebo (73 patients).
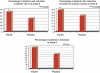
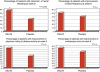
Results: In all, 65 patients in the VSL#3 group and 66 patients in the placebo group completed the study. The decrease in ulcerative colitis disease activity index (UCDAI) scores of 50% or more was higher in the VSL#3 group than in the placebo group (63.1 vs. 40.8; per protocol (PP) P=0.010, confidence interval (CI)₉₅(%) 0.51-0.74; intention to treat (ITT) P=0.031, CI₉₅(%) 0.47-0.69). Significant results with VSL#3 were recorded in an improvement of three points or more in the UCDAI score (60.5% vs. 41.4%; PP P=0.017, CI₉₅(%) 0.51-0.74; ITT P=0.046, CI₉₅(%) 0.47-0.69) and in rectal bleeding (PP P=0.014, CI₉₅(%) 0.46-0.70; ITT P=0.036, CI₉₅(%) 0.41-0.65), whereas stool frequency (PP P=0.202, CI₉₅(%) 0.39-0.63; ITT P=0.229, CI₉₅(%) 0.35-0.57), physician's rate of disease activity (PP P=0.088, CI₉₅(%) 0.34-0.58; ITT P=0.168, CI₉₅(%) 0.31-0.53), and endoscopic scores (PP P=0.086, CI₉₅(%) 0.74-0.92; ITT P=0.366, CI₉₅(%) 0.66-0.86) did not show statistical differences. Remission was higher in the VSL#3 group than in the placebo group (47.7% vs. 32.4%; PP P=0.069, CI₉₅(%) 0.36-0.60; ITT P=0.132, CI₉₅(%) 0.33-0.56). Eight patients on VSL#3 (11.2%) and nine patients on placebo (12.3%) reported mild side effects.
Conclusions: VSL#3 supplementation is safe and able to reduce UCDAI scores in patients affected by relapsing mild-to-moderate UC who are under treatment with 5-ASA and/or immunosuppressants. Moreover, VSL#3 improves rectal bleeding and seems to reinduce remission in relapsing UC patients after 8 weeks of treatment, although these parameters do not reach statistical significance.
Figures
Comment in
-
Treatment with the probiotic VSL#3 as an adjunctive therapy in relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis significantly reduces ulcerative colitis disease activity.Evid Based Med. 2011 Aug;16(4):108-9. doi: 10.1136/ebm1189. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Evid Based Med. 2011. PMID: 21354984 No abstract available.
-
VSL#3 and remission in active ulcerative colitis: larger studies required.Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Mar;106(3):547; author reply 547-8. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.451. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21378771 No abstract available.
-
VSL#3 for ulcerative colitis: growing evidence?Gastroenterology. 2011 May;140(5):1685-6; discussion 1686-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.03.032. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21440588 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The probiotic preparation, VSL#3 induces remission in patients with mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Nov;7(11):1202-9, 1209.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.016. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19631292 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a probiotic preparation (VSL#3) on induction and maintenance of remission in children with ulcerative colitis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Feb;104(2):437-43. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2008.118. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19174792 Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotics for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 4;3(3):CD005573. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005573.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32128795 Free PMC article.
-
VSL#3 probiotic mixture: a review of its use in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.Drugs. 2006;66(10):1371-87. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200666100-00006. Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16903771 Review.
-
Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD000543. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000543.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4:CD000543. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000543.pub4. PMID: 23076889 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the effects of combined treatment of mesalazine with Lactobacillus casei in the experimental model of ulcerative colitis.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Oct 3;11:1456053. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1456053. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39421689 Free PMC article.
-
Ulcerative colitis: molecular insights and intervention therapy.Mol Biomed. 2024 Oct 10;5(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00207-w. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39384730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are Small Molecules Effective in Treating Inflammatory Pouch Disorders Following Ileal Pouch-Anal Anastomosis for Ulcerative Colitis? Here Is Where We Stand.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 17;14(9):1164. doi: 10.3390/biom14091164. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of probiotics supplementation in gastrointestinal complications and quality of life of patients with systemic sclerosis: A systematic review.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 13;10(16):e36230. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36230. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39247342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of probiotics in IBD: An overview of systematic reviews and updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.United European Gastroenterol J. 2024 Sep;12(7):960-981. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12636. Epub 2024 Aug 6. United European Gastroenterol J. 2024. PMID: 39106167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz M, Cohen R. Optimizing conventional therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2008;10:585–590. - PubMed
-
- Travis S, Stange EF, Lémann M, et al. For the European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). European evidence-based consensus of the management of ulcerative colitis: current management. J Crohn Colitis. 2008;2:24–62. - PubMed
-
- Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, et al. Oral bacteriotherapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:305–309. - PubMed
-
- Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Helwig U, et al. Prophylaxis of pouchitis onset with probiotic therapy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1202–1209. - PubMed
-
- Tursi A, Brandimarte G, Giorgetti GM, et al. Low-dose balsalazide plus a high-potency probiotic preparation is more effective than balsalazide alone or mesalazine in the treatment of acute mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis. Med Sci Monit. 2004;10:PI126–PI131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

