WASH and WAVE actin regulators of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family are controlled by analogous structurally related complexes
- PMID: 20498093
- PMCID: PMC2890800
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913293107
WASH and WAVE actin regulators of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family are controlled by analogous structurally related complexes
Abstract
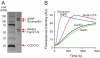
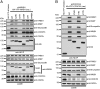
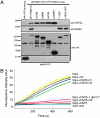
We recently showed that the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family member, WASH, localizes to endosomal subdomains and regulates endocytic vesicle scission in an Arp2/3-dependent manner. Mechanisms regulating WASH activity are unknown. Here we show that WASH functions in cells within a 500 kDa core complex containing Strumpellin, FAM21, KIAA1033 (SWIP), and CCDC53. Although recombinant WASH is constitutively active toward the Arp2/3 complex, the reconstituted core assembly is inhibited, suggesting that it functions in cells to regulate actin dynamics through WASH. FAM21 interacts directly with CAPZ and inhibits its actin-capping activity. Four of the five core components show distant (approximately 15% amino acid sequence identify) but significant structural homology to components of a complex that negatively regulates the WASP family member, WAVE. Moreover, biochemical and electron microscopic analyses show that the WASH and WAVE complexes are structurally similar. Thus, these two distantly related WASP family members are controlled by analogous structurally related mechanisms. Strumpellin is mutated in the human disease hereditary spastic paraplegia, and its link to WASH suggests that misregulation of actin dynamics on endosomes may play a role in this disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
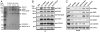
Similar articles
-
Multiple repeat elements within the FAM21 tail link the WASH actin regulatory complex to the retromer.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jun;23(12):2352-61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-12-1059. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22513087 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin polymerization by plant proteins distantly related to Scar/WAVE.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 16;101(46):16379-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407392101. Epub 2004 Nov 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15534215 Free PMC article.
-
WASP family proteins: Molecular mechanisms and implications in human disease.Eur J Cell Biol. 2022 Jun-Aug;101(3):151244. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2022.151244. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Eur J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35667337 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the regulation and cellular functions of the ARP2/3 complex.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;14(1):7-12. doi: 10.1038/nrm3492. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23212475 Review.
-
Regulation of actin dynamics by WASP family proteins.J Biochem. 2003 Sep;134(3):309-13. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvg146. J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14561714 Review.
Cited by
-
Strumpellin and Spartin, Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Proteins, are Binding Partners.J Exp Neurosci. 2015 May 7;9:15-25. doi: 10.4137/JEN.S22969. eCollection 2015. J Exp Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25987849 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the eukaryotic ARP2/3 activators of the WASP family: WASP, WAVE, WASH, and WHAMM, and the proposed new family members WAWH and WAML.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Feb 8;5:88. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-88. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 22316129 Free PMC article.
-
FAM21 is critical for TLR2/CLEC4E-mediated dendritic cell function against Candida albicans.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Jan 30;6(4):e202201414. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201414. Print 2023 Apr. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 36717248 Free PMC article.
-
The spectrum of KIAA0196 variants, and characterization of a murine knockout: implications for the mutational mechanism in hereditary spastic paraplegia type SPG8.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Nov 16;10:147. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0359-x. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 26572744 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Retromer Complex in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Mar 1;8:42. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00042. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26973516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takenawa T, Suetsugu S. The WASP–WAVE protein network: connecting the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(1):37–48. - PubMed
-
- Eden S, Rohatgi R, Podtelejnikov AV, Mann M, Kirschner MW. Mechanism of regulation of WAVE1-induced actin nucleation by Rac1 and Nck. Nature. 2002;418(6899):790–793. - PubMed
-
- Stradal TE, Scita G. Protein complexes regulating Arp2/3-mediated actin assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18(1):4–10. - PubMed
-
- Derivery E, Lombard B, Loew D, Gautreau A. The Wave complex is intrinsically inactive. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66(10):777–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

