The Ca(2+) -dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPK-independent salt-stress acclimation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 20497378
- PMCID: PMC2988408
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04257.x
The Ca(2+) -dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPK-independent salt-stress acclimation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
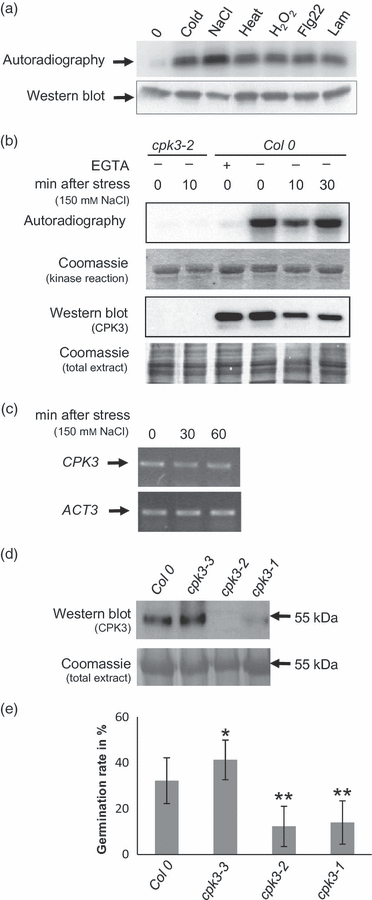
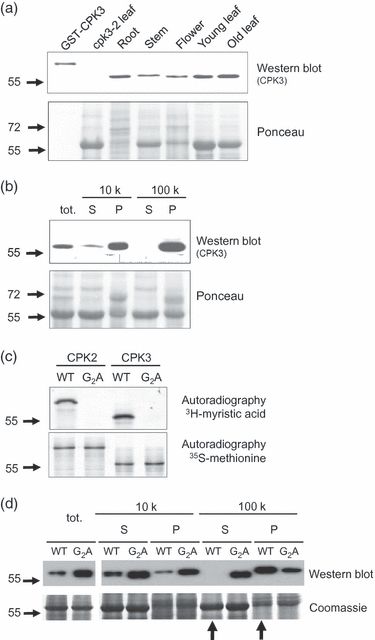
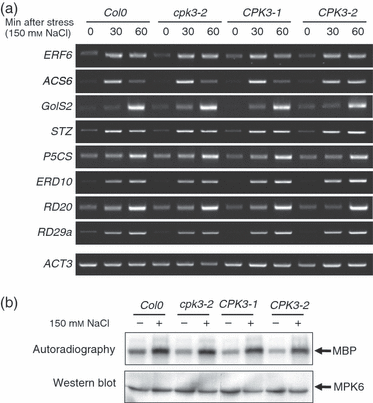
Plants use different signalling pathways to respond to external stimuli. Intracellular signalling via calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) or mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) present two major pathways that are widely used to react to a changing environment. Both CDPK and MAPK pathways are known to be involved in the signalling of abiotic and biotic stresses in animal, yeast and plant cells. Here, we show the essential function of the CDPK CPK3 (At4g23650) for salt stress acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana, and test crosstalk between CPK3 and the major salt-stress activated MAPKs MPK4 and MPK6 in the salt stress response. CPK3 kinase activity was induced by salt and other stresses after transient overexpression in Arabidopsis protoplasts, but endogenous CPK3 appeared to be constitutively active in roots and leaves in a strictly Ca(2+) -dependent manner. cpk3 mutants show a salt-sensitive phenotype comparable with mutants in MAPK pathways. In contrast to animal cells, where crosstalk between Ca(2+) and MAPK signalling is well established, CPK3 seems to act independently of those pathways. Salt-induced transcriptional induction of known salt stress-regulated and MAPK-dependent marker genes was not altered, whereas post-translational protein phosphorylation patterns from roots of wild type and cpk3 plants revealed clear differences. A significant portion of CPK3 was found to be associated with the plasma membrane and the vacuole, both depending on its N-terminal myristoylation. An initial proteomic study led to the identification of 28 potential CPK3 targets, predominantly membrane-associated proteins.
Keywords: Ca2+-dependent protein kinase; MAP kinase; N-myristoylation; crosstalk; protein phosphorylation; salt stress adaptation.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal compilation © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salt stress triggers phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis vacuolar K+ channel TPK1 by calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs).Mol Plant. 2013 Jul;6(4):1274-1289. doi: 10.1093/mp/sss158. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23253603 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk of calcium-dependent protein kinase and MAP kinase signaling.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Jan;6(1):8-12. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.1.14012. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21248475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis CPK3 plays extensive roles in various biological and environmental responses.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Oct;5(10):1263-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.10.12957. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20798597 Free PMC article.
-
CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell S-type anion- and Ca(2+)-permeable channels and stomatal closure.PLoS Biol. 2006 Oct;4(10):e327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040327. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 17032064 Free PMC article.
-
Modes of MAPK substrate recognition and control.Trends Plant Sci. 2015 Jan;20(1):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Trends Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25301445 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of CDPKs in plant development, nutrient and stress signaling.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 30;13:996203. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.996203. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase in maize.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 1;14:433. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-433. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23815483 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis Ca2+-Dependent Protein Kinase CPK12 Is Involved in Plant Response to Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 14;19(12):4062. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124062. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30558245 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK) in grass Brachypodium distachyon.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jan 16;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6475-6. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31948407 Free PMC article.
-
CDPK1 from ginger promotes salinity and drought stress tolerance without yield penalty by improving growth and photosynthesis in Nicotiana tabacum.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 23;8(10):e76392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076392. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24194837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agell N, Bachs O, Rocamora N, Villalonga P. Modulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by Ca(2+), and calmodulin. Cell. Signal. 2002;14:649–654. - PubMed
-
- Aitken A. Functional specificity in 14-3-3 isoform interactions through dimer formation and phosphorylation. Chromosome location of mammalian isoforms and variants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002;50:993–1010. - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, et al. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 2003;301:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science. 1999;285:1256–1258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

