A global protein kinase and phosphatase interaction network in yeast
- PMID: 20489023
- PMCID: PMC3983991
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1176495
A global protein kinase and phosphatase interaction network in yeast
Abstract
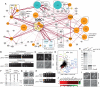
The interactions of protein kinases and phosphatases with their regulatory subunits and substrates underpin cellular regulation. We identified a kinase and phosphatase interaction (KPI) network of 1844 interactions in budding yeast by mass spectrometric analysis of protein complexes. The KPI network contained many dense local regions of interactions that suggested new functions. Notably, the cell cycle phosphatase Cdc14 associated with multiple kinases that revealed roles for Cdc14 in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, the DNA damage response, and metabolism, whereas interactions of the target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) uncovered new effector kinases in nitrogen and carbon metabolism. An extensive backbone of kinase-kinase interactions cross-connects the proteome and may serve to coordinate diverse cellular responses.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cell signaling. Signaling through cooperation.Science. 2010 May 21;328(5981):983-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1190993. Science. 2010. PMID: 20489011 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cell signaling. Signaling through cooperation.Science. 2010 May 21;328(5981):983-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1190993. Science. 2010. PMID: 20489011 No abstract available.
-
Evolution of Ime2 phosphorylation sites on Cdk1 substrates provides a mechanism to limit the effects of the phosphatase Cdc14 in meiosis.Mol Cell. 2007 Mar 9;25(5):689-702. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.012. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17349956 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc14 Phosphatase Promotes TORC1-Regulated Autophagy in Yeast.J Mol Biol. 2018 May 25;430(11):1671-1684. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 22. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29694832
-
Closing mitosis: the functions of the Cdc14 phosphatase and its regulation.Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:203-32. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.093051. Annu Rev Genet. 2004. PMID: 15568976 Review.
-
Phosphatases, DNA damage checkpoints and checkpoint deactivation.Cell Cycle. 2007 Dec 15;6(24):3058-64. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.24.5100. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 18075314 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitation of the dynamic profiles of the innate immune response using multiplex selected reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Jun;12(6):1513-29. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.023465. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23418394 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interaction networks: probing disease mechanisms using model systems.Genome Med. 2013 Apr 30;5(4):37. doi: 10.1186/gm441. eCollection 2013. Genome Med. 2013. PMID: 23635424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria to nucleus signaling and the role of ceramide in its integration into the suite of cell quality control processes during aging.Ageing Res Rev. 2015 Sep;23(Pt A):67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2014.12.007. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Ageing Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25555678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational and informatics strategies for identification of specific protein interaction partners in affinity purification mass spectrometry experiments.Proteomics. 2012 May;12(10):1639-55. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100537. Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22611043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ait1 regulates TORC1 signaling and localization in budding yeast.Elife. 2022 Sep 1;11:e68773. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68773. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36047762 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

