Downregulation of robust acute type I interferon responses distinguishes nonpathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection of natural hosts from pathogenic SIV infection of rhesus macaques
- PMID: 20484518
- PMCID: PMC2897601
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02612-09
Downregulation of robust acute type I interferon responses distinguishes nonpathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection of natural hosts from pathogenic SIV infection of rhesus macaques
Abstract
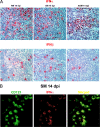
The mechanisms underlying the AIDS resistance of natural hosts for simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) remain unknown. Recently, it was proposed that natural SIV hosts avoid disease because their plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are intrinsically unable to produce alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) in response to SIV RNA stimulation. However, here we show that (i) acute SIV infections of natural hosts are associated with a rapid and robust type I IFN response in vivo, (ii) pDCs are the principal in vivo producers of IFN-alpha/beta at peak acute infection in lymphatic tissues, and (iii) natural SIV hosts downregulate these responses in early chronic infection. In contrast, persistently high type I IFN responses are observed during pathogenic SIV infection of rhesus macaques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of type I interferon-associated viral sensing during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection in African green monkeys.J Virol. 2015 Jan;89(1):751-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02430-14. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25355871 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-encoded TLR ligands reveal divergent functional responses of mononuclear phagocytes in pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus infection.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2188-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201645. Epub 2013 Jan 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23338235 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between simian immunodeficiency virus RNA levels and the mRNA levels of alpha/beta interferons (IFN-alpha/beta) and IFN-alpha/beta-inducible Mx in lymphoid tissues of rhesus macaques during acute and chronic infection.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(16):8433-45. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.16.8433-8445.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12134046 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology of natural simian immunodeficiency virus infections.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2012 Jan;7(1):71-8. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32834dde01. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22134342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generalized immune activation and innate immune responses in simian immunodeficiency virus infection.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011 Sep;6(5):411-8. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e3283499cf6. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21743324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Induced Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Associated With Monocyte Activation and Predicts Viral Load.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 5;11(8):ofae434. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae434. eCollection 2024 Aug. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39104769 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Tat Protein Activates both the MyD88 and TRIF Pathways To Induce Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Interleukin-10 in Human Monocytes.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):5886-5898. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00262-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27053552 Free PMC article.
-
Type I IFN signaling blockade by a PASylated antagonist during chronic SIV infection suppresses specific inflammatory pathways but does not alter T cell activation or virus replication.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Aug 24;14(8):e1007246. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007246. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30142226 Free PMC article.
-
T cell activation is insufficient to drive SIV disease progression.JCI Insight. 2023 Jul 24;8(14):e161111. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.161111. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37485874 Free PMC article.
-
Primate lentiviruses are differentially inhibited by interferon-induced transmembrane proteins.Virology. 2015 Jan 1;474:10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.10.015. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25463599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosinger, S. E., Q. Li, S. N. Gordon, N. R. Klatt, L. Duan, L. Xu, N. Francella, A. Sidahmed, A. J. Smith, E. M. Cramer, M. Zeng, D. Masopust, J. V. Carlis, L. Ran, T. H. Vanderford, M. Paiardini, R. B. Isett, D. A. Baldwin, J. G. Else, S. I. Staprans, G. Silvestri, A. T. Haase, and D. J. Kelvin. 2009. Global genomic analysis reveals rapid control of a robust innate response in SIV-infected sooty mangabeys. J. Clin. Invest. 119:3556-3572. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. M., M. Paiardini, K. S. Knox, A. I. Asher, B. Cervasi, T. E. Asher, P. Scheinberg, D. A. Price, C. A. Hage, L. M. Kholi, A. Khoruts, I. Frank, J. Else, T. Schacker, G. Silvestri, and D. C. Douek. 2008. Differential Th17 CD4 T-cell depletion in pathogenic and nonpathogenic lentiviral infections. Blood 112:2826-2835. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cella, M., D. Jarrossay, F. Facchetti, O. Alebardi, H. Nakajima, A. Lanzavecchia, and M. Colonna. 1999. Plasmacytoid monocytes migrate to inflamed lymph nodes and produce large amounts of type I interferon. Nat. Med. 5:919-923. - PubMed
-
- Estes, J. D., S. N. Gordon, M. Zeng, A. M. Chahroudi, R. M. Dunham, S. I. Staprans, C. S. Reilly, G. Silvestri, and A. T. Haase. 2008. Early resolution of acute immune activation and induction of PD-1 in SIV-infected sooty mangabeys distinguishes nonpathogenic from pathogenic infection in rhesus macaques. J. Immunol. 180:6798-6807. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

