MOF and histone H4 acetylation at lysine 16 are critical for DNA damage response and double-strand break repair
- PMID: 20479123
- PMCID: PMC2897562
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01476-09
MOF and histone H4 acetylation at lysine 16 are critical for DNA damage response and double-strand break repair
Abstract
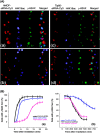
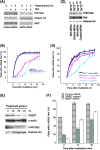
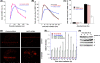
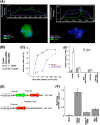
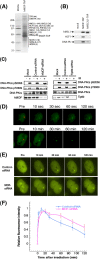
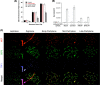
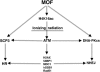
The human MOF gene encodes a protein that specifically acetylates histone H4 at lysine 16 (H4K16ac). Here we show that reduced levels of H4K16ac correlate with a defective DNA damage response (DDR) and double-strand break (DSB) repair to ionizing radiation (IR). The defect, however, is not due to altered expression of proteins involved in DDR. Abrogation of IR-induced DDR by MOF depletion is inhibited by blocking H4K16ac deacetylation. MOF was found to be associated with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs), a protein involved in nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair. ATM-dependent IR-induced phosphorylation of DNA-PKcs was also abrogated in MOF-depleted cells. Our data indicate that MOF depletion greatly decreased DNA double-strand break repair by both NHEJ and homologous recombination (HR). In addition, MOF activity was associated with general chromatin upon DNA damage and colocalized with the synaptonemal complex in male meiocytes. We propose that MOF, through H4K16ac (histone code), has a critical role at multiple stages in the cellular DNA damage response and DSB repair.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bisbenzamidine derivative, pentamidine represses DNA damage response through inhibition of histone H2A acetylation.Mol Cancer. 2010 Feb 9;9:34. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-34. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20144237 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PKcs and ATM co-regulate DNA double-strand break repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Aug 6;8(8):920-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.05.006. Epub 2009 Jun 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19535303 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of heterochromatin on DSB repair.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Jun;37(Pt 3):569-76. doi: 10.1042/BST0370569. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19442252
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
-
Tip60: connecting chromatin to DNA damage signaling.Cell Cycle. 2010 Mar 1;9(5):930-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.5.10931. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20160506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting of Nrf2 induces DNA damage signaling and protects colonic epithelial cells from ionizing radiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 23;109(43):E2949-55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207718109. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23045680 Free PMC article.
-
The Chromatin Landscape around DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Yeast and Its Influence on DNA Repair Pathway Choice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3248. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043248. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H3K9me3 and H4K20me3 represent the epigenetic landscape for 53BP1 binding to DNA lesions.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Oct 11;10(10):2585-2605. doi: 10.18632/aging.101572. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 30312172 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1/PARP1 crosstalk: connecting DNA damage and metabolism.Genome Integr. 2013 Dec 20;4(1):6. doi: 10.1186/2041-9414-4-6. Genome Integr. 2013. PMID: 24360018 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design and validation of a Tip60 histone acetyltransferase inhibitor.Sci Rep. 2014 Jun 20;4:5372. doi: 10.1038/srep05372. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24947938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal, M., S. Pandita, C. R. Hunt, A. Gupta, X. Yue, S. Khan, R. K. Pandita, D. Pratt, J. W. Shay, J. S. Taylor, and T. K. Pandita. 2008. Inhibition of telomerase activity enhances hyperthermia-mediated radiosensitization. Cancer Res. 68:3370-3378. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar, A., and P. B. Becker. 2000. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 5:367-375. - PubMed
-
- Allfrey, V. G., B. G. Pogo, V. C. Littau, E. L. Gershey, and A. E. Mirsky. 1968. Histone acetylation in insect chromosomes. Science 159:314-316. - PubMed
-
- Andegeko, Y., L. Moyal, L. Mittelman, I. Tsarfaty, Y. Shiloh, and G. Rotman. 2001. Nuclear retention of ATM at sites of DNA double strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 276:38224-38230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R13 CA130756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA130756-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034746-05S1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA130756-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-06/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA130756-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034746/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MOP-64289/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- CA 50519/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034746-06/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA10445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA130756-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA123232/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 64289-2/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R37 CA050519/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034746-05/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034746-06S1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129537-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123232-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 87253-1/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R13 CA130756-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050519/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
