Nuclear trafficking of the epidermal growth factor receptor family membrane proteins
- PMID: 20473332
- PMCID: PMC2904849
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.157
Nuclear trafficking of the epidermal growth factor receptor family membrane proteins
Abstract
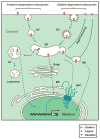
Multiple membrane-bound receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB-2, have been reported to be localized in the nucleus, where emerging evidence suggests that they are involved in transcriptional regulation, cell proliferation, DNA repair and chemo- and radio-resistance. Recent studies have shown that endocytosis and endosomal sorting are involved in the nuclear transport of cell surface RTKs. However, the detailed mechanism by which the full-length receptors embedded in the endosomal membrane travel all the way from the cell surface to the early endosomes and pass through the nuclear pore complexes is unknown. This important area has been overlooked for decades, which has hindered progress in our understanding of nuclear RTKs' functions. Here, we discuss the putative mechanisms by which EGFR family RTKs are shuttled into the nucleus. Understanding the trafficking mechanisms as to how RTKs are transported from the cell surface to the nucleus will significantly contribute to understanding the functions of the nuclear RTKs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family.Cell Biosci. 2012 Apr 20;2(1):13. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-13. Cell Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22520625 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-bound trafficking regulates nuclear transport of integral epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB-2.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16869-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.314799. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22451678 Free PMC article.
-
The translocon Sec61beta localized in the inner nuclear membrane transports membrane-embedded EGF receptor to the nucleus.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 3;285(49):38720-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.158659. Epub 2010 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20937808 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor tyrosine kinase transport and functions in cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2020;147:59-107. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32593407 Review.
-
The NAE Pathway: Autobahn to the Nucleus for Cell Surface Receptors.Cells. 2019 Aug 16;8(8):915. doi: 10.3390/cells8080915. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31426451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family.Cell Biosci. 2012 Apr 20;2(1):13. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-13. Cell Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22520625 Free PMC article.
-
EGFs and ERBBs--brief history and prospects.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Dec;21(9):917-21. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20970513 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism for the anticancer activity of aspirin and salicylates.Int J Oncol. 2019 Apr;54(4):1256-1270. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4701. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30720135 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2017 May 17;9(5):52. doi: 10.3390/cancers9050052. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28513565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical signaling mode of the epidermal growth factor receptor family.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Sep 15;5(10):2944-58. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26693051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam RM, Danciu T, McLellan DL, Borer JG, Lin J, Zurakowski D, et al. A nuclear form of the heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor precursor is a feature of aggressive transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Arasada RR, Carpenter G. Secretase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Mdm2 by the ErbB-4 intracellular domain fragment. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:30783–30787. - PubMed
-
- Bailey KE, Costantini DL, Cai Z, Scollard DA, Chen Z, Reilly RM, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition modulates the nuclear localization and cytotoxicity of the Auger electron emitting radiopharmaceutical 111In-DTPA human epidermal growth factor. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:1562–1570. - PubMed
-
- Baldys A, Raymond JR. Critical role of ESCRT machinery in EGFR recycling. Biochemistry. 2009;48:9321–9323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

