Dendritic cells in uninfected infants born to hepatitis B virus-positive mothers
- PMID: 20463102
- PMCID: PMC2897267
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00074-10
Dendritic cells in uninfected infants born to hepatitis B virus-positive mothers
Abstract
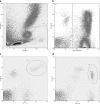
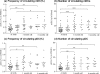
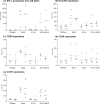
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) play a central role in antiviral immunity, detecting viruses via Toll-like receptors (TLR) and producing in response vast amounts of type I interferons (IFNs). Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes chronic infection after vertical transmission. This study investigated whether an HBV-infected maternal environment might influence DC numbers and pDC function in uninfected infants. Blood was collected from inactive HBsAg carrier and control mothers and their infants at birth and 1 and 6 months of age. HBV DNA was measured in maternal and neonatal perinatal sera using real-time PCR. The circulating frequencies of myeloid DCs (mDCs) and pDCs were determined in the babies by flow cytometry. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and cord blood pDCs were stimulated with resiquimod, and alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) production and the pDC phenotype were assessed. The effect of the common-cold virus, rhinovirus (RV), on resiquimod stimulation was also determined. HBV DNA was detected in 62.3% of the mothers and 41% of their infants. DC numbers and pDC functions were similar between subjects and controls and were not correlated with maternal or neonatal viremia. RV infection did not induce pDC maturation until the age of 6 months, and it reduced TLR7-dependent resiquimod-induced IFN-alpha production similarly in both groups. Although the DC system is immature at birth, DCs of uninfected neonates of HBV-positive mothers are competent to initiate and maintain T-cell responses. RV is a weak inducer of IFN-alpha production until the age of 6 months and inhibits IFN-alpha responses triggered by the TLR7 pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissecting the dendritic cell controversy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Cell Mol Immunol. 2015 May;12(3):283-91. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.95. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25363524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR7/TLR8 Activation Restores Defective Cytokine Secretion by Myeloid Dendritic Cells but Not by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in HIV-Infected Pregnant Women and Newborns.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e67036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067036. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826189 Free PMC article.
-
Frequencies of dendritic cells and Toll-like receptor 3 in neonates born to HBsAg-positive mothers with different HBV serological profiles.Epidemiol Infect. 2015 Jan;143(1):62-70. doi: 10.1017/S0950268814000624. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Epidemiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 24650439 Free PMC article.
-
Serological positive markers of hepatitis B virus in femoral venous blood or umbilical cord blood should not be evidence of in-utero infection among neonates.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 12;16(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1754-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27515176 Free PMC article.
-
#38: Hepatitis B in pregnancy screening, treatment, and prevention of vertical transmission.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Jan;214(1):6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.09.100. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 26454123 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota modulate the immune effect against hepatitis B virus infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Nov;34(11):2139-47. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2464-0. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26272175 Review.
-
The immune tolerant phase of chronic HBV infection: new perspectives on an old concept.Cell Mol Immunol. 2015 May;12(3):258-63. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.79. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25176526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the dendritic cell controversy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Cell Mol Immunol. 2015 May;12(3):283-91. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.95. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25363524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-Dependent Immune Events during HBV Infection from Birth to Adulthood: An Alternative Interpretation.Front Immunol. 2014 Sep 23;5:441. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00441. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25295036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerance and immunity to pathogens in early life: insights from HBV infection.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Nov;39(6):643-652. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0641-1. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28685270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beasley, R. P., L. Y. Hwang, C. C. Lin, Y. C. Ko, and S. J. Twu. 1983. Incidence of hepatitis among students at a university in Taiwan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 117:213-222. - PubMed
-
- Delespesse, G., L. P. Yang, Y. Ohshima, C. Demeure, U. Shu, D. G. Byun, and M. Sarfati. 1998. Maturation of human neonatal CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes into Th1/Th2 effectors. Vaccine 16:1415-1419. - PubMed
-
- De Wit, D., V. Olislagers, S. Goriely, F. Vermeulen, H. Wagner, M. Goldman, and F. Willems. 2004. Blood plasmacytoid dendritic cell responses to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides are impaired in human newborns. Blood 103:1030-1032. - PubMed
-
- Diebold, S., T. Kaisho, H. Hemmi, S. Akira, and C. Reis e Sousa. 2004. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303:1529-1531. - PubMed
-
- Duan, X., M. Wang, H. Li, H. Zhuang, D. Xu, and F. Wang. 2004. Decreased frequency and function of circulating plasmocytoid dendritic cells (pDC) in hepatitis B virus infected humans. J. Clin. Immunol. 24:637-646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

