Targeting the dimerization of epidermal growth factor receptors with small-molecule inhibitors
- PMID: 20456371
- PMCID: PMC2906783
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.00986.x
Targeting the dimerization of epidermal growth factor receptors with small-molecule inhibitors
Abstract
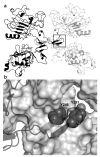
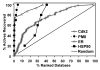
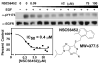
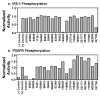
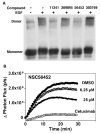
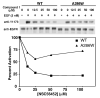
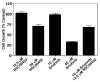
The epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in the control of cell proliferation, and its overexpression is strongly associated with a variety of aggressive cancers. For example, 70-80% of metaplastic (cancer cells of mixed type) breast carcinomas overexpress EGF receptors. In addition, the EGF receptor is a highly significant contributor to common brain tumors (glioblastoma multiforme), both in initiation and progression (Huang P.H., Xu A.M., White F.M. (2009) Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signal;2:re6.). Brain metastases, an unmet medical need, are also common in metastatic cancer associated with overexpression of EGF receptors. Formation of EGF receptor homodimers is essential for kinase activation and was the basis for exploring direct inhibition of EGF receptor activation by blocking dimerization with small molecules. While inhibitors of protein/protein interactions are often considered difficult therapeutic targets, NSC56452, initially identified by virtual screening, was shown experimentally to inhibit EGF receptor kinase activation in a dose-dependent manner. This compound blocked EGF-stimulated dimer formation as measured by chemical cross-linking and luciferase fragment complementation. The compound was further shown to inhibit the growth of HeLa cells. This first-generation lead compound represents the first drug-like, small-molecule inhibitor of EGF receptor activation that is not directed against the intracellular kinase domain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review on EGFR Inhibitors: Critical Updates.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16(14):1134-66. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160321114917. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26996617 Review.
-
Allosteric regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligand binding by tyrosine kinase inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 31;293(35):13401-13414. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004139. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29997256 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanics of EGF receptor/ErbB2 kinase activation revealed by luciferase fragment complementation imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jan 3;109(1):137-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111316109. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22190492 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for kinase-mediated dimerization of the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 2;287(45):38244-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414391. Epub 2012 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22988250 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:395-411. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30500458 Review.
Cited by
-
Afatinib and Temozolomide combination inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting EGFRvIII-cMet signaling in glioblastoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 18;38(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1264-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31215502 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches in NSCLC Targeting K-RAS and EGFR.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 14;20(22):5701. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225701. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31739412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of protein-protein interaction of HER2-EGFR and HER2-HER3 by a rationally designed peptidomimetic.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012;30(5):594-606. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2012.687525. Epub 2012 Jun 26. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012. PMID: 22731912 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and characterization of peptidomimetic conjugate of BODIPY targeting HER2 protein extracellular domain.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Jul;65:60-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.04.038. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23688700 Free PMC article.
-
Luciferase fragment complementation imaging in preclinical cancer studies.Oncoscience. 2014 Jun 1;1(5):310-25. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.45. eCollection 2014. Oncoscience. 2014. PMID: 25594026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell DW, Gore I, Okimoto RA, Godin-Heymann N, Sordella R, Mulloy R, Sharma SV, Brannigan BW, Mohapatra G, Settleman J, Haber DA. Inherited susceptibility to lung cancer may be associated with the T790M drug resistance mutation in EGFR. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1315–1316. - PubMed
-
- Bishop PC, Myers T, Robey R, Fry DW, Liu ET, Blagosklonny MV, Bates SE. Differential sensitivity of cancer cells to inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Oncogene. 2002;21:119–127. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Lyne PD, Giordanetto F, Lovell T, Li J. On Evaluating Molecular-Docking Methods for Pose Prediction and Enrichment Factors. J Chem Inf Model. 2006;46:401–415. - PubMed
-
- Clayton AHA, Walker F, Orchard SG, Henderson C, Fuchs D, Rothacker J, Nice EC, Burgess AW. Ligand-induced Dimer-Tetramer Transition during the Activation of the Cell Surface Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-A Multidimensional Microscopy Analysis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:30392–30399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

