GSK3beta and beta-catenin modulate radiation cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 20454507
- PMCID: PMC2864473
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.92112
GSK3beta and beta-catenin modulate radiation cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Knowledge of factors and mechanisms contributing to the inherent radioresistance of pancreatic cancer may improve cancer treatment. Irradiation inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) by phosphorylation at serine 9. In turn, release of cytosolic membrane beta-catenin with subsequent nuclear translocation promotes survival. Both GSK3beta and beta-catenin have been implicated in cancer cell proliferation and resistance to death.
Methods: We investigated pancreatic cancer cell survival after radiation in vitro and in vivo, with a particular focus on the role of the function of the GSK3beta/beta-catenin axis.
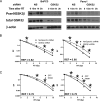
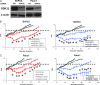
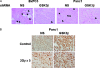
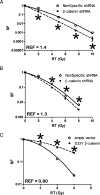
Results: Lithium chloride, RNAi-medicated silencing of GSK3beta, or the expression of a kinase dead mutant GSK3beta resulted in radioresistance of Panc1 and BxPC3 pancreatic cancer cells. Conversely, ectopic expression of a constitutively active form of GSK3beta resulted in radiosensitization of Panc1 cells. GSK3beta silencing increased radiation-induced beta-catenin target gene expression as measured by studies of AXIN2 and LEF1 transcript levels. Western blot analysis of total and phosphorylated levels of GSK3beta and beta-catenin showed that GSK3beta inhibition resulted in stabilization of beta-catenin. Xenografts of both BxPC3 and Panc1 with targeted silencing of GSK3beta exhibited radioresistance in vivo. Silencing of beta-catenin resulted in radiosensitization, whereas a nondegradable beta-catenin construct induced radioresistance.
Conclusions: These data support the hypothesis that GSK3beta modulates the cellular response to radiation in a beta-catenin-dependent mechanism. Further understanding of this pathway may enhance the development of clinical trials combining drugs inhibiting beta-catenin activation with radiation and chemotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Figures
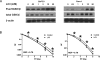
Similar articles
-
MiR-744 increases tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):37557-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5317. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26485754 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PPARα by clofibrate sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to radiation through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Oncogene. 2018 Feb 15;37(7):953-962. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.401. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29059162
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibition sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine.J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;47(3):321-33. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0484-9. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22041920
-
GSK3β as a novel promising target to overcome chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer.Drug Resist Updat. 2021 Sep;58:100779. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2021.100779. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Drug Resist Updat. 2021. PMID: 34461526 Review.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: can it be a target for oral cancer.Mol Cancer. 2010 Jun 11;9:144. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-144. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20537194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming intratumor heterogeneity of polygenic cancer drug resistance with improved biomarker integration.Neoplasia. 2012 Dec;14(12):1278-89. doi: 10.1593/neo.122096. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 23308059 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer induces changes in the expression of nuclear β-catenin: prognostic significance.BMC Cancer. 2014 Mar 15;14:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-192. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24629143 Free PMC article.
-
Raman spectroscopy and group and basis-restricted non negative matrix factorisation identifies radiation induced metabolic changes in human cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 16;11(1):3853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83343-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33594122 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Sensitizes Esophageal Cancer Cells to Chemoradiotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10301. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910301. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638639 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Signaling in the Breast: From Development to Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 18;10:884467. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.884467. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35663403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Macdonald JS, McCoy S, Whitehead RP, Iqbal S, Wade JL, III, Giguere JK, Abbruzzese JL. A phase II study of farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777 in pancreatic cancer: a Southwest oncology group, (SWOG 9924) study. Invest New Drugs. 2005;23:485–487. - PubMed
-
- Jones L, Ghaneh P, Humphreys M, Neoptolemos JP. The matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;880:288–307. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–1966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
