PML nuclear bodies
- PMID: 20452955
- PMCID: PMC2857171
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000661
PML nuclear bodies
Abstract
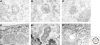
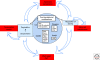
PML nuclear bodies are matrix-associated domains that recruit an astonishing variety of seemingly unrelated proteins. Since their discovery in the early 1960s, PML bodies have fascinated cell biologists because of their beauty and their tight association with cellular disorders. The identification of PML, a gene involved in an oncogenic chromosomal translocation, as the key organizer of these domains drew instant interest onto them. The multiple levels of PML body regulation by a specific posttranslational modification, sumoylation, have raised several unsolved issues. Functionally, PML bodies may sequester, modify or degrade partner proteins, but in many ways, PML bodies still constitute an enigma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting promyelocytic leukemia protein: a means to regulating PML nuclear bodies.Int J Biol Sci. 2009 May 22;5(4):366-76. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5.366. Int J Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19471587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of component exchange at PML nuclear bodies.J Cell Sci. 2008 Aug 15;121(Pt 16):2731-43. doi: 10.1242/jcs.031922. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18664490
-
Histone deacetylase 7 promotes PML sumoylation and is essential for PML nuclear body formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5658-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00874-08. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625722 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the C-terminal regions of promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) isoforms II and V to PML nuclear body formation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 31;287(36):30729-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.374769. Epub 2012 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22773875 Free PMC article.
-
Pondering the puzzle of PML (promyelocytic leukemia) nuclear bodies: can we fit the pieces together using an RNA regulon?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Nov;1783(11):2145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.06.005. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18616965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A History over 60 Years-From the Most Malignant to the most Curable Form of Acute Leukemia.Oncol Ther. 2019 Jun;7(1):33-65. doi: 10.1007/s40487-018-0091-5. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Oncol Ther. 2019. PMID: 32700196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YB-1 functions as a porter to lead influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes to microtubules.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(20):11086-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00453-12. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22855482 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SUMOylation in full antiestrogenicity.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(19):3823-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00290-12. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22826433 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere Maintenance in Pediatric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 20;20(23):5836. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235836. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31757062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper Tolerance Mechanism of the Novel Marine Multi-Stress Tolerant Yeast Meyerozyma guilliermondii GXDK6 as Revealed by Integrated Omics Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 18;12:771878. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.771878. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34867906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batty E, Jensen K, Freemont P 2009. PML nuclear bodies and their spatial relationships in the mammalian cell nucleus. Front Biosci 14:1182–1196 - PubMed
-
- Beech SJ, Lethbridge KJ, Killick N, McGlincy N, Leppard KN 2005. Isoforms of the promyelocytic leukemia protein differ in their effects on ND10 organization. Exp Cell Res 307:109–117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
