Association of human cytomegalovirus proteins IRS1 and TRS1 with the viral DNA polymerase accessory subunit UL44
- PMID: 20444996
- PMCID: PMC3052514
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.022640-0
Association of human cytomegalovirus proteins IRS1 and TRS1 with the viral DNA polymerase accessory subunit UL44
Abstract
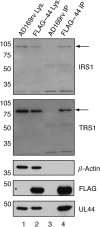
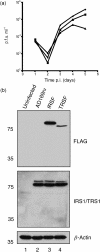
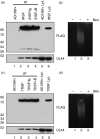
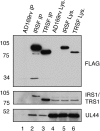
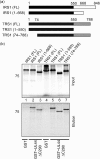
Multiple proteins interacting with DNA polymerases orchestrate DNA replication. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) encodes a DNA polymerase that includes the presumptive processivity factor UL44. UL44 is structurally homologous to the eukaryotic DNA polymerase processivity factor proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), which interacts with numerous proteins. Previous proteomic analysis has identified the HCMV protein IRS1 as a candidate protein interacting with UL44. Nuclease-resistant reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation of UL44 with IRS1 and with TRS1, which has an amino terminus identical to that of IRS1, was observed from lysate of cells infected with viruses expressing epitope-tagged UL44, epitope-tagged IRS1 or epitope-tagged TRS1. Western blotting of protein immunoprecipitated from infected cell lysate indicated that epitope-tagged IRS1 and TRS1 do not associate simultaneously with UL44. Glutathione S-transferase pull-down experiments indicated that IRS1 and TRS1 interact with UL44 via a region that is identical in both proteins. Taken together, these data suggest that IRS1 and TRS1 may compete for association with UL44 and may affect UL44 function differentially.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the association of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase subunit UL44 with the viral DNA replication factor UL84.J Virol. 2009 Aug;83(15):7581-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00663-09. Epub 2009 May 20. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19457994 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin associates with the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase accessory subunit UL44 and is necessary for efficient viral replication.J Virol. 2010 Feb;84(4):1771-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01510-09. Epub 2009 Dec 9. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20007282 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation deleting sequences encoding the amino terminus of human cytomegalovirus UL84 impairs interaction with UL44 and capsid localization.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(20):11066-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01379-12. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22855486 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase processivity factor UL44 is modified by SUMO in a DNA-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049630. Epub 2012 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166733 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of immediate early proteins encoded by the human cytomegalovirus UL36-38, UL115-119, TRS1/IRS1 and US3 loci.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):350-60. doi: 10.1159/000150506. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130045 Review.
Cited by
-
Host cell nucleolin is required to maintain the architecture of human cytomegalovirus replication compartments.mBio. 2012 Feb 7;3(1):e00301-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00301-11. Print 2012. mBio. 2012. PMID: 22318319 Free PMC article.
-
The life cycle and pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus infection: lessons from proteomics.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014 Dec;11(6):697-711. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2014.971116. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25327590 Free PMC article.
-
Cis and trans acting factors involved in human cytomegalovirus experimental and natural latent infection of CD14 (+) monocytes and CD34 (+) cells.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003366. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003366. Epub 2013 May 23. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23717203 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insights into the Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/v15081703. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonism of the protein kinase R pathway by the guinea pig cytomegalovirus US22-family gene gp145.Virology. 2012 Nov 10;433(1):157-66. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Virology. 2012. PMID: 22917493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appleton, B. A., Loregian, A., Filman, D. J., Coen, D. M. & Hogle, J. M. (2004). The cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase subunit UL44 forms a C clamp-shaped dimer. Mol Cell 15, 233–244. - PubMed
-
- Appleton, B. A., Brooks, J., Loregian, A., Filman, D. J., Coen, D. M. & Hogle, J. M. (2006). Crystal structure of the cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase subunit UL44 in complex with the C terminus from the catalytic subunit. Differences in structure and function relative to unliganded UL44. J Biol Chem 281, 5224–5232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

