Structural dynamics in DNA damage signaling and repair
- PMID: 20439160
- PMCID: PMC2916978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.03.012
Structural dynamics in DNA damage signaling and repair
Abstract
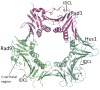
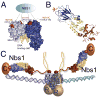
Changing macromolecular conformations and complexes are critical features of cellular networks, typified by DNA damage response pathways that are essential to life. These fluctuations enhance the specificity of macromolecular recognition and catalysis, and enable an integrated functioning of pathway components, ensuring efficiency while reducing off pathway reactions. Such dynamic complexes challenge classical detailed structural analyses, so their characterizations demand combining methods that provide detail with those that inform dynamics in solution. Small-angle X-ray scattering, electron microscopy, hydrogen-deuterium exchange and computation are complementing detailed structures from crystallography and NMR to provide comprehensive models for DNA damage searching, specificity, signaling, and repair. Here, we review new approaches and results on DNA damage responses that advance structural biology in the fourth dimension, connecting proteins to pathways.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

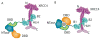
Similar articles
-
What Combined Measurements From Structures and Imaging Tell Us About DNA Damage Responses.Methods Enzymol. 2017;592:417-455. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 May 29. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28668129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) combined with crystallography and computation: defining accurate macromolecular structures, conformations and assemblies in solution.Q Rev Biophys. 2007 Aug;40(3):191-285. doi: 10.1017/S0033583507004635. Q Rev Biophys. 2007. PMID: 18078545 Review.
-
Bridging the solution divide: comprehensive structural analyses of dynamic RNA, DNA, and protein assemblies by small-angle X-ray scattering.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010 Feb;20(1):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.12.015. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2010. PMID: 20097063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intricate structural chemistry of base excision repair machinery: implications for DNA damage recognition, removal, and repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Apr 1;6(4):410-28. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.10.004. Epub 2007 Jan 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17208522 Review.
-
Envisioning the dynamics and flexibility of Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex to decipher its roles in DNA replication and repair.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;117(2-3):182-193. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.12.004. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25576492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Double strand binding-single strand incision mechanism for human flap endonuclease: implications for the superfamily.Mech Ageing Dev. 2012 Apr;133(4):195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.11.009. Epub 2012 Jan 8. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012. PMID: 22244820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fidelity of the ligation step determines how ends are resolved during nonhomologous end joining.Nat Commun. 2014 Jul 3;5:4286. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5286. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24989324 Free PMC article.
-
An S/T-Q cluster domain census unveils new putative targets under Tel1/Mec1 control.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 23;13:664. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-664. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23176708 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural biology of DNA repair: spatial organisation of the multicomponent complexes of nonhomologous end joining.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Aug 25;2010:621695. doi: 10.4061/2010/621695. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20862368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hitomi K, Iwai S, Tainer JA. The intricate structural chemistry of base excision repair machinery: implications for DNA damage recognition, removal, and repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2007;6:410–428. - PubMed
-
- Garcin ED, Hosfield DJ, Desai SA, Haas BJ, Bjoras M, Cunningham RP, Tainer JA. DNA apurinic-apyrimidinic site binding and excision by endonuclease IV. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:515–522. The endonuclease IV structures and mutational analyses provide experimental evidence for strain in BER backbone incision and for stable product complexes that aid handoffs without the release of toxic DNA repair intermediates. - PubMed
-
- Chapados BR, Hosfield DJ, Han S, Qiu J, Yelent B, Shen B, Tainer JA. Structural basis for FEN-1 substrate specificity and PCNA-mediated activation in DNA replication and repair. Cell. 2004;116:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Pascal JM, Tsodikov OV, Hura GL, Song W, Cotner EA, Classen S, Tomkinson AE, Tainer JA, Ellenberger T. A flexible interface between DNA ligase and PCNA supports conformational switching and efficient ligation of DNA. Mol Cell. 2006;24:279–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

