NLRC5 negatively regulates the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways
- PMID: 20434986
- PMCID: PMC3150216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.040
NLRC5 negatively regulates the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways
Abstract
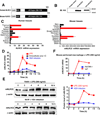
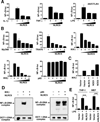
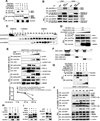
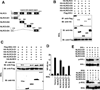
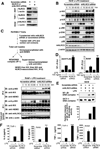
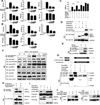
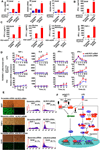
Stringent control of the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways is critical to effective host immune responses, yet the molecular mechanisms that negatively regulate these pathways are poorly understood. Here, we show that NLRC5, a member of the highly conserved NOD-like protein family, can inhibit the IKK complex and RIG-I/MDA5 function. NLRC5 inhibited NF-kappaB-dependent responses by interacting with IKKalpha and IKKbeta and blocking their phosphorylation. It also interacted with RIG-I and MDA5, but not with MAVS, to inhibit RLR-mediated type I interferon responses. Consistent with these observations, NLRC5-specific siRNA knockdown not only enhanced the activation of NF-kappaB and its responsive genes, TNF-alpha and IL-6, but also promoted type I interferon signaling and antiviral immunity. Our findings identify NLRC5 as a negative regulator that blocks two central components of the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways and suggest an important role for NLRC5 in homeostatic control of innate immunity.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced TLR-induced NF-κB signaling and type I interferon responses in NLRC5 deficient mice.Cell Res. 2012 May;22(5):822-35. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.53. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22473004 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory NLRs Control the RLR-Mediated Type I Interferon and Inflammatory Responses in Human Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 5;9:2314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02314. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30344524 Free PMC article.
-
Oyster Versatile IKKα/βs Are Involved in Toll-Like Receptor and RIG-I-Like Receptor Signaling for Innate Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 31;10:1826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01826. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31417578 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune responses against protozoan parasites: a focus on the emerging role of Nod-like receptors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Aug;73(16):3035-51. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2212-3. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27032699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting edge: impaired MHC class I expression in mice deficient for Nlrc5/class I transactivator.J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):516-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200064. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22711889 Free PMC article.
-
NLRC5 PANoptosome: Aquaman of the Dead Sea.Cell Res. 2025 Jan;35(1):9-10. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-01011-5. Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 39112672 No abstract available.
-
NLRC5 regulates expression of MHC-I and provides a target for anti-tumor immunity in transmissible cancers.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Jul;147(7):1973-1991. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03601-x. Epub 2021 Apr 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33797607 Free PMC article.
-
Holding the inflammatory system in check: NLRs keep it cool.F1000Prime Rep. 2015 Feb 3;7:15. doi: 10.12703/P7-15. eCollection 2015. F1000Prime Rep. 2015. PMID: 25750733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Shaw MH, Kim YG, Nunez G. NOD-like receptors: role in innate immunity and inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:365–398. - PubMed
-
- Cui S, Eisenacher K, Kirchhofer A, Brzozka K, Lammens A, Lammens K, Fujita T, Conzelmann KK, Krug A, Hopfner KP. The C-terminal regulatory domain is the RNA 5'-triphosphate sensor of RIG-I. Mol Cell. 2008;29:169–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA121191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA09327/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA101795-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121191-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA090327-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116408/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA101795/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA101795/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA094237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA116408/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA094237-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752-04S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116408-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090327/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA094237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

