Parkinson's disease: insights from pathways
- PMID: 20421364
- PMCID: PMC2875048
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq167
Parkinson's disease: insights from pathways
Abstract
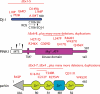
Parkinson's disease (PD) typically presents in sporadic fashion, but the identification of disease-causing mutations in monogenically inherited PD genes has provided crucial insight into the pathogenesis of this disorder. Mutations in autosomal recessively inherited genes, namely parkin, PINK1 and DJ-1, typically lead to early onset parkinsonism. At least two of these genes (PINK1 and parkin) appear to work in the same pathway related to maintenance of mitochondrial functional integrity under conditions of oxidative stress. Dominantly inherited mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) and alpha-synuclein cause late onset PD, generally with Lewy bodies that are characteristic of sporadic PD and there is evidence that these two genes are also in a common pathway. There is also growing evidence from recently undertaken genome-wide association studies that naturally occurring sequence variants in alpha-synuclein and LRRK2, but also Tau, also confer an increased risk for late onset, sporadic PD. Collectively, these results highlight how understanding pathways for inherited PD are starting to impact ideas about the pathogenesis, some of which may also be relevant to the commoner sporadic disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
What genetics tells us about the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson's disease.Physiol Rev. 2011 Oct;91(4):1161-218. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2010. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22013209 Review.
-
Analysis of LRRK2, SNCA, Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 in Zambian patients with Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012 Jun;18(5):567-71. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012. PMID: 22445250
-
Clinical genetics of Parkinson's disease and related disorders.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007;13 Suppl 3:S229-32. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(08)70007-5. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007. PMID: 18267241 Review.
-
Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and function in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.Exp Neurol. 2009 Aug;218(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.03.006. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19303005 Review.
-
New aspects of genetic contributions to Parkinson's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;24(3):417-24. doi: 10.1385/JMN:24:3:417. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15655263 Review.
Cited by
-
Progressive degeneration of human neural stem cells caused by pathogenic LRRK2.Nature. 2012 Nov 22;491(7425):603-7. doi: 10.1038/nature11557. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23075850 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 (MARK2) turns on phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) at Thr-313, a mutation site in Parkinson disease: effects on mitochondrial transport.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8174-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.262287. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22238344 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening Platforms in the Discovery of Novel Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;8(2):30. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8020030. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection of Indole-Derivative Compound NC001-8 by the Regulation of the NRF2 Pathway in Parkinson's Disease Cell Models.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:5074367. doi: 10.1155/2019/5074367. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781339 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of lysosomal alpha-galactosiase A gene in sporadic Parkinson's disease.Neurochem Res. 2011 Oct;36(10):1939-44. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0516-0. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21643977
References
-
- Polymeropoulos M.H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S.E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., Root H., Rubenstein J., Boyer R., et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. doi:10.1126/science.276.5321.2045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spillantini M.G., Schmidt M.L., Lee V.M., Trojanowski J.Q., Jakes R., Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388:839–840. doi:10.1038/42166. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gasser T. Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009;11:e22. doi:10.1017/S1462399409001148. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardy J., Lewis P., Revesz T., Lees A., Paisan-Ruiz C. The genetics of Parkinson's syndromes: a critical review. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009;19:254–265. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hatano T., Kubo S., Sato S., Hattori N. Pathogenesis of familial Parkinson's disease: new insights based on monogenic forms of Parkinson's disease. J. Neurochem. 2009;111:1075–1093. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06403.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

