Targeting mTOR: prospects for mTOR complex 2 inhibitors in cancer therapy
- PMID: 20418915
- PMCID: PMC3031870
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.139
Targeting mTOR: prospects for mTOR complex 2 inhibitors in cancer therapy
Abstract
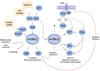
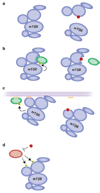
Small molecule inhibitors that selectively target cancer cells and not normal cells would be valuable anti-cancer therapeutics. The mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) is emerging as a promising candidate target for such an inhibitor. Recent studies in cancer biology indicate that mTORC2 activity is essential for the transformation and vitality of a number of cancer cell types, but in many normal cells, mTORC2 activity is less essential. These studies are intensifying interest in developing inhibitors that specifically target mTORC2. However, there are many open questions regarding the function and regulation of mTORC2 and its function in both normal and cancer cells. Here, we summarize exciting new research into the biology of mTORC2 signaling and highlight the current state and future prospects for mTOR-targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeted Inhibition of Rictor/mTORC2 in Cancer Treatment: A New Era after Rapamycin.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(4):288-304. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666151113120830. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26563881 Review.
-
Targeting mTOR globally in cancer: thinking beyond rapamycin.Cell Cycle. 2009 Dec;8(23):3831-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.23.10070. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19901542 Review.
-
Active-site inhibitors of mTOR target rapamycin-resistant outputs of mTORC1 and mTORC2.PLoS Biol. 2009 Feb 10;7(2):e38. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000038. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19209957 Free PMC article.
-
TORC-specific phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): phospho-Ser2481 is a marker for intact mTOR signaling complex 2.Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;69(5):1821-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3014. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19244117 Free PMC article.
-
The mTOR pathway: a new target in cancer therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Aug;10(5):484-95. doi: 10.2174/156800910791517172. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20384580 Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR: a link from the extracellular milieu to transcriptional regulation of oligodendrocyte development.ASN Neuro. 2013 Mar 19;5(1):e00108. doi: 10.1042/AN20120092. ASN Neuro. 2013. PMID: 23421405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Target therapy in metastatic pheochromocytoma: current perspectives and controversies.Oncol Rev. 2014 Sep 23;8(2):249. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2014.249. eCollection 2014 Sep 23. Oncol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25992237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two hits are better than one: targeting both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin as a therapeutic strategy for acute leukemia treatment.Oncotarget. 2012 Apr;3(4):371-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.477. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22564882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of selective inhibitors targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 14;8(11):e80070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080070. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244612 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jul 15;10(14):2305-16. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.14.16586. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21670596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

