Structural basis for Fe-S cluster assembly and tRNA thiolation mediated by IscS protein-protein interactions
- PMID: 20404999
- PMCID: PMC2854127
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000354
Structural basis for Fe-S cluster assembly and tRNA thiolation mediated by IscS protein-protein interactions
Abstract
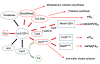
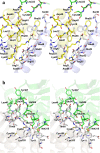
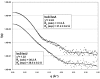
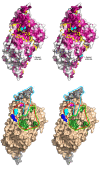
The cysteine desulfurase IscS is a highly conserved master enzyme initiating sulfur transfer via persulfide to a range of acceptor proteins involved in Fe-S cluster assembly, tRNA modifications, and sulfur-containing cofactor biosynthesis. Several IscS-interacting partners including IscU, a scaffold for Fe-S cluster assembly; TusA, the first member of a sulfur relay leading to sulfur incorporation into the wobble uridine of several tRNAs; ThiI, involved in tRNA modification and thiamine biosynthesis; and rhodanese RhdA are sulfur acceptors. Other proteins, such as CyaY/frataxin and IscX, also bind to IscS, but their functional roles are not directly related to sulfur transfer. We have determined the crystal structures of IscS-IscU and IscS-TusA complexes providing the first insight into their different modes of binding and the mechanism of sulfur transfer. Exhaustive mutational analysis of the IscS surface allowed us to map the binding sites of various partner proteins and to determine the functional and biochemical role of selected IscS and TusA residues. IscS interacts with its partners through an extensive surface area centered on the active site Cys328. The structures indicate that the acceptor proteins approach Cys328 from different directions and suggest that the conformational plasticity of a long loop containing this cysteine is essential for the ability of IscS to transfer sulfur to multiple acceptor proteins. The sulfur acceptors can only bind to IscS one at a time, while frataxin and IscX can form a ternary complex with IscU and IscS. Our data support the role of frataxin as an iron donor for IscU to form the Fe-S clusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
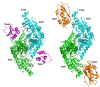
Comment in
-
Synopsis. Multiple sulfur acceptors dock at IscS.PLoS Biol. 2010 Apr 13;8(4):e1000353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000353. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20405048 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
TusA influences Fe-S cluster assembly and iron homeostasis in E. coli by reducing the translation efficiency of Fur.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0055624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00556-24. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38916309 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of IscU and TusA to different but competing sites of IscS influences the activity of IscS and directs sulfur to the respective biomolecular synthesis pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 9;12(8):e0094924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00949-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38980029 Free PMC article.
-
The SufE sulfur-acceptor protein contains a conserved core structure that mediates interdomain interactions in a variety of redox protein complexes.J Mol Biol. 2004 Nov 19;344(2):549-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.074. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15522304
-
Metamorphic protein IscU alternates conformations in the course of its role as the scaffold protein for iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis and delivery.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 17;587(8):1172-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 16. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23333622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared-intermediates in the biosynthesis of thio-cofactors: Mechanism and functions of cysteine desulfurases and sulfur acceptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1853(6):1470-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.10.018. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25447671 Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA1006 is a persulfide-modified protein that is critical for molybdenum homeostasis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055593. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409003 Free PMC article.
-
CyaY and TusA regulate ISC- and SUF-mediated l-cysteine desulfurase activity.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Sep 27;5(11):1165-76. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00225c. Online ahead of print. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39372677 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical discrimination between selenium and sulfur 1: a single residue provides selenium specificity to human selenocysteine lyase.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030581. Epub 2012 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22295093 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of client-the scaffold on which FeS clusters are build-with J-domain protein Hsc20 and its evolving Hsp70 partners.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 12;9:1034453. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1034453. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36310602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly (CIA) system: factors, mechanism, and relevance to cellular iron regulation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 27;285(35):26745-26751. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R110.122218. Epub 2010 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20522543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mueller E. G. Trafficking in persulfides: delivering sulfur in biosynthetic pathways. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:185–194. - PubMed
-
- Kessler D. Enzymatic activation of sulfur for incorporation into biomolecules in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006;30:825–840. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D. C, Dean D. R, Smith A. D, Johnson M. K. Structure, function, and formation of biological iron-sulfur clusters. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:247–281. - PubMed
-
- Fontecave M, Ollagnier-de-Choudens S. Iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis in bacteria: mechanisms of cluster assembly and transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;474:226–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

