Binding of the complexin N terminus to the SNARE complex potentiates synaptic-vesicle fusogenicity
- PMID: 20400951
- PMCID: PMC3172005
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1791
Binding of the complexin N terminus to the SNARE complex potentiates synaptic-vesicle fusogenicity
Abstract
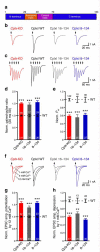
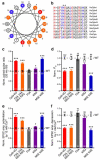
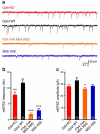
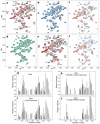
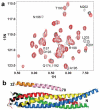
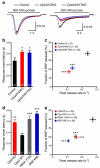
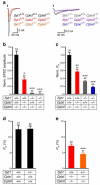
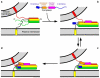
Complexins facilitate and inhibit neurotransmitter release through distinct domains, and their function was proposed to be coupled to the Ca(2+) sensor synaptotagmin-1 (Syt1). However, the mechanisms underlying complexin function remain unclear. We now uncover an interaction between the complexin N terminus and the SNARE complex C terminus, and we show that disrupting this interaction abolishes the facilitatory function of complexins in mouse neurons. Analyses of hypertonically induced exocytosis show that complexins enhance synaptic-vesicle fusogenicity. Genetic experiments crossing complexin- and Syt1-null mice indicate a functional interaction between these proteins but also show that complexins can promote Ca(2+)-triggered release in the absence of Syt1. We propose that the complexin N terminus stabilizes the SNARE complex C terminus and/or helps release the inhibitory function of complexins, thereby activating the fusion machinery in a manner that may cooperate with Syt1 but does not require Syt1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C-terminal complexin sequence is selectively required for clamping and priming but not for Ca2+ triggering of synaptic exocytosis.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 22;32(8):2877-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3360-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22357870 Free PMC article.
-
A complexin/synaptotagmin 1 switch controls fast synaptic vesicle exocytosis.Cell. 2006 Sep 22;126(6):1175-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.030. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16990140
-
The primed SNARE-complexin-synaptotagmin complex for neuronal exocytosis.Nature. 2017 Aug 24;548(7668):420-425. doi: 10.1038/nature23484. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28813412 Free PMC article.
-
Models of synaptotagmin-1 to trigger Ca2+ -dependent vesicle fusion.FEBS Lett. 2018 Nov;592(21):3480-3492. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13193. Epub 2018 Jul 30. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 30004579 Review.
-
For better or for worse: complexins regulate SNARE function and vesicle fusion.Traffic. 2008 Sep;9(9):1403-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00758.x. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18445121 Review.
Cited by
-
Vesicle trafficking and vesicle fusion: mechanisms, biological functions, and their implications for potential disease therapy.Mol Biomed. 2022 Sep 21;3(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s43556-022-00090-3. Mol Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36129576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ablation of All Synaptobrevin vSNAREs Blocks Evoked But Not Spontaneous Neurotransmitter Release at Neuromuscular Synapses.J Neurosci. 2019 Jul 31;39(31):6049-6066. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0403-19.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 3. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31160536 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread occurrence of the droplet state of proteins in the human proteome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 29;117(52):33254-33262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007670117. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33318217 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoscale architecture of synaptic vesicles and scaffolding complexes revealed by cryo-electron tomography.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 2;121(27):e2403136121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403136121. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38923992 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal complexin sequence is selectively required for clamping and priming but not for Ca2+ triggering of synaptic exocytosis.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 22;32(8):2877-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3360-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22357870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jahn R, Scheller RH. SNAREs - engines for membrane fusion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:631–43. - PubMed
-
- Wojcik SM, Brose N. Regulation of membrane fusion in synaptic excitation-secretion coupling: speed and accuracy matter. Neuron. 2007;55:11–24. - PubMed
-
- McMahon HT, Missler M, Li C, Sudhof TC. Complexins: cytosolic proteins that regulate SNAP receptor function. Cell. 1995;83:111–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

