TCR stimulation drives cleavage and shedding of the ITIM receptor CD31
- PMID: 20400708
- PMCID: PMC3110943
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902219
TCR stimulation drives cleavage and shedding of the ITIM receptor CD31
Abstract
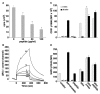
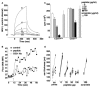
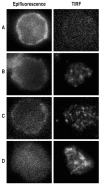
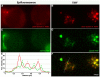
CD31 is a transmembrane molecule endowed with T cell regulatory functions owing to the presence of 2 immunotyrosine-based inhibitory motifs. For reasons not understood, CD31 is lost by a portion of circulating T lymphocytes, which appear prone to uncontrolled activation. In this study, we show that extracellular T cell CD31 comprising Ig-like domains 1 to 5 is cleaved and shed from the surface of human T cells upon activation via their TCR. The shed CD31 can be specifically detected as a soluble, truncated protein in human plasma. CD31 shedding results in the loss of its inhibitory function because the necessary cis-homo-oligomerization of the molecule, triggered by the trans-homophilic engagement of the distal Ig-like domain 1, cannot be established by CD31(shed) cells. However, we show that a juxta-membrane extracellular sequence, comprising part of the domain 6, remains expressed at the surface of CD31(shed) T cells. We also show that the immunosuppressive CD31 peptide aa 551-574 is highly homophilic and possibly acts by homo-oligomerizing with the truncated CD31 remaining after its cleavage and shedding. This peptide is able to sustain phosphorylation of the CD31 ITIM(686) and of SHP2 and to inhibit TCR-induced T cell activation. Finally, systemic administration of the peptide in BALB/c mice efficiently suppresses Ag-induced T cell-mediated immune responses in vivo. We conclude that the loss of T cell regulation caused by CD31 shedding driven by TCR stimulation can be rescued by molecular tools able to engage the truncated juxta-membrane extracellular molecule that remains exposed at the surface of CD31(shed) cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Primed T cell responses to chemokines are regulated by the immunoglobulin-like molecule CD31.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039433. Epub 2012 Jun 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22724015 Free PMC article.
-
Upholding the T cell immune-regulatory function of CD31 inhibits the formation of T/B immunological synapses in vitro and attenuates the development of experimental autoimmune arthritis in vivo.J Autoimmun. 2015 Jan;56:23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 25277651
-
Lck is required for activation-induced T cell death after TCR ligation with partial agonists.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1437-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1437. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734719
-
An immunologist's guide to CD31 function in T-cells.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jun 1;126(Pt 11):2343-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.124099. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23761922 Review.
-
T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) transmembrane peptides: A new paradigm for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Apr-Jun;4(2):273-83. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.2.11909. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20431344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primed T cell responses to chemokines are regulated by the immunoglobulin-like molecule CD31.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039433. Epub 2012 Jun 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22724015 Free PMC article.
-
The CD31 molecule: a possible neuroprotective agent in acute ischemic stroke?Thromb J. 2017 Apr 13;15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12959-017-0134-4. eCollection 2017. Thromb J. 2017. PMID: 28413360 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized risk predictor for acute cellular rejection in lung transplant using soluble CD31.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 21;12(1):17628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21070-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36271122 Free PMC article.
-
Cleaved CD31 as a target for in vivo molecular imaging of inflammation.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56163-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31863037 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide binding to cleaved CD31 dampens ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal injury.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2018 Aug 15;6(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40635-018-0192-3. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2018. PMID: 30112663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newman PJ, Berndt MC, Gorski J, White GC, 2nd, Lyman S, Paddock C, Muller WA. PECAM-1 (CD31) cloning and relation to adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Science. 1990;247:1219–1222. - PubMed
-
- Tada Y, Koarada S, Morito F, Ushiyama O, Haruta Y, Kanegae F, Ohta A, Ho A, Mak TW, Nagasawa K. Acceleration of the onset of collagen-induced arthritis by a deficiency of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:3280–3290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

